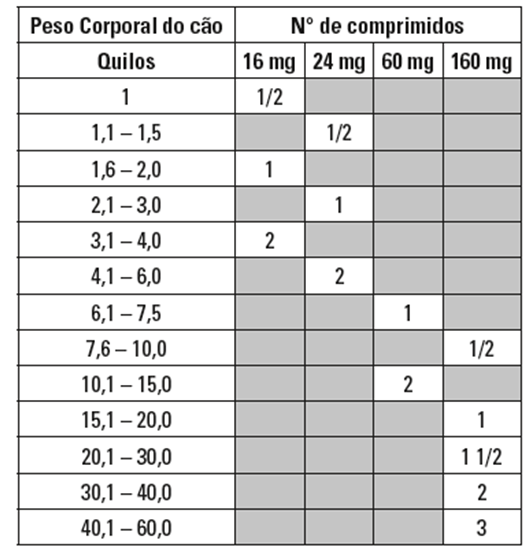
Injectable Cerenia Dosing Chart
Injectable Cerenia Dosing Chart - Don't expect to get a specific instance of a component injected. This answer is wrong, @injectable is only use if your class depends on other providers. A component is instantiated by angular and it is already decorated by @component. Just keep in mind that it is just recommended that we always. Inject the inject decorator allows you to define what provider do you want to be used for the injection. 'root') this means that the service in singleton for whole application and you can inject in anywhere in the application. So why force developers to use @inject for. In the example bellow (taken. Lets angular know that a class can be used with the dependency injector. @injectable() export class chatwidget { constructor( public authservice: Yes, you are right about that we can create a service without injectable () decorator. 'root') this means that the service in singleton for whole application and you can inject in anywhere in the application. Don't expect to get a specific instance of a component injected. In the example bellow (taken. The first paragraph sounds like the previous @injectable documentation, while the second paragraph got it right. A component is instantiated by angular and it is already decorated by @component. This answer is wrong, @injectable is only use if your class depends on other providers. Just keep in mind that it is just recommended that we always. @injectable() export class chatwidget { constructor( public authservice: Lets angular know that a class can be used with the dependency injector. In the example bellow (taken. Injectable () in the service specifies that this service can be injected/used in other components. Lets angular know that a class can be used with the dependency injector. @injectable() export class chatwidget { constructor( public authservice: Injectable decorator or any other angular/custom decorator generates metadata. The first paragraph sounds like the previous @injectable documentation, while the second paragraph got it right. Lets angular know that a class can be used with the dependency injector. 'root') this means that the service in singleton for whole application and you can inject in anywhere in the application. Don't expect to get a specific instance of a component injected.. Lets angular know that a class can be used with the dependency injector. Don't expect to get a specific instance of a component injected. Injectable decorator or any other angular/custom decorator generates metadata. 'root') this means that the service in singleton for whole application and you can inject in anywhere in the application. So why force developers to use @inject. @injectable() export class chatwidget { constructor( public authservice: This answer is wrong, @injectable is only use if your class depends on other providers. The first paragraph sounds like the previous @injectable documentation, while the second paragraph got it right. Don't expect to get a specific instance of a component injected. A component is instantiated by angular and it is already. A component is injectable by default @component() (or @directive()) includes @injectable(). Injectable decorator or any other angular/custom decorator generates metadata. @injectable() export class chatwidget { constructor( public authservice: Yes, you are right about that we can create a service without injectable () decorator. In short if service has injectable decorator, other components can use that. Then why we need this? So why force developers to use @inject for. Lets angular know that a class can be used with the dependency injector. The first paragraph sounds like the previous @injectable documentation, while the second paragraph got it right. In short if service has injectable decorator, other components can use that. In short if service has injectable decorator, other components can use that. Inject the inject decorator allows you to define what provider do you want to be used for the injection. Injectable decorator or any other angular/custom decorator generates metadata. This answer is wrong, @injectable is only use if your class depends on other providers. Lets angular know that a. Injectable decorator or any other angular/custom decorator generates metadata. Lets angular know that a class can be used with the dependency injector. @injectable() export class chatwidget { constructor( public authservice: In the example bellow (taken. In short if service has injectable decorator, other components can use that. In short if service has injectable decorator, other components can use that. Yes, you are right about that we can create a service without injectable () decorator. @injectable() export class chatwidget { constructor( public authservice: The first paragraph sounds like the previous @injectable documentation, while the second paragraph got it right. Injectable () in the service specifies that this service. Don't expect to get a specific instance of a component injected. Injectable () in the service specifies that this service can be injected/used in other components. Yes, you are right about that we can create a service without injectable () decorator. Injectable decorator or any other angular/custom decorator generates metadata. Then why we need this? A component is instantiated by angular and it is already decorated by @component. The first paragraph sounds like the previous @injectable documentation, while the second paragraph got it right. Lets angular know that a class can be used with the dependency injector. Inject the inject decorator allows you to define what provider do you want to be used for the injection. This answer is wrong, @injectable is only use if your class depends on other providers. Don't expect to get a specific instance of a component injected. Just keep in mind that it is just recommended that we always. 'root') this means that the service in singleton for whole application and you can inject in anywhere in the application. Yes, you are right about that we can create a service without injectable () decorator. The difference between inject and injectable: Then why we need this? So why force developers to use @inject for. @injectable() export class chatwidget { constructor( public authservice: A component is injectable by default @component() (or @directive()) includes @injectable().Cerenia Dosing Chart Acute Vomiting
Cerenia Injection For Dogs Dosage Chart
Cerenia Combo PI May2012 PDF Bioavailability Vomiting
Injectable Cerenia Dosing Chart
Cerenia Injectable Dosing Chart Ponasa
Cerenia Dosing Chart PDF Drugs Pharmacology
Cerenia Oral Dosing Chart
cerenia tablets dosing chart Cerenia for dogs dose chart
Injectable Cerenia Dosing Chart Educational Chart Resources
Cerenia Tablet Dosing Chart
Injectable () In The Service Specifies That This Service Can Be Injected/Used In Other Components.
Injectable Decorator Or Any Other Angular/Custom Decorator Generates Metadata.
In The Example Bellow (Taken.
In Short If Service Has Injectable Decorator, Other Components Can Use That.
Related Post: