Skull Identification Chart
Skull Identification Chart - It is divided into two main parts: The skull is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain. The cranium, which encases the brain, and the facial skeleton, which supports. It is comprised of many bones, formed by intramembranous ossification, which are. Commonly expresses figurative death, e.g., dying from extreme laughter, frustration, or affection. The human skull consists of 22 bones (or 29, including the inner ear bones and hyoid bone) which are mostly connected together by ossified joints, so called sutures. There are 29 bones (including the hyoid and. The skull forms the frontmost portion of the axial skeleton and is a product of cephalization and vesicular enlargement of the brain, with several special senses structures such as the eyes,. The skull is one of the most vital bony structures of the human body, as it houses and protects the most important organs, including the brain. Learn a skull anatomy with parts, names & detailed diagram. The skull is a bony structure that supports the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. Commonly expresses figurative death, e.g., dying from extreme laughter, frustration, or affection. Your skull is the part of your skeleton that holds and protects your brain. The skull is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain. There are 29 bones (including the hyoid and. Learn a skull anatomy with parts, names & detailed diagram. It also holds or supports several of your main sensory organs, like your eyes, ears,. The human skull consists of 22 bones (or 29, including the inner ear bones and hyoid bone) which are mostly connected together by ossified joints, so called sutures. Skull, skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, composed of bones or cartilage, which form a unit that protects the brain and some sense organs. The skull forms the frontmost portion of the axial skeleton and is a product of cephalization and vesicular enlargement of the brain, with several special senses structures such as the eyes,. Complete guide for students to explore structure & function of the human skull. It is divided into two main parts: It is comprised of many bones, formed by intramembranous ossification, which are. Commonly expresses figurative death, e.g., dying from extreme laughter, frustration, or affection. The skull is one of the most vital bony structures of the human body, as it. It is divided into two main parts: The skull is a bony framework of the head, consisting of 22 bones. The skull is one of the most vital bony structures of the human body, as it houses and protects the most important organs, including the brain. Skull, skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, composed of bones or cartilage, which. The skull is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain. Complete guide for students to explore structure & function of the human skull. The skull is a bony structure that supports the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. The skull forms the frontmost portion of the axial skeleton and is. Commonly expresses figurative death, e.g., dying from extreme laughter, frustration, or affection. The cranium, which encases the brain, and the facial skeleton, which supports. Skull, skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, composed of bones or cartilage, which form a unit that protects the brain and some sense organs. The human skull consists of 22 bones (or 29, including the. The skull is one of the most vital bony structures of the human body, as it houses and protects the most important organs, including the brain. It is divided into two main parts: Commonly expresses figurative death, e.g., dying from extreme laughter, frustration, or affection. It also holds or supports several of your main sensory organs, like your eyes, ears,.. The skull is a bony framework of the head, consisting of 22 bones. The skull is one of the most vital bony structures of the human body, as it houses and protects the most important organs, including the brain. Commonly expresses figurative death, e.g., dying from extreme laughter, frustration, or affection. The skull is the skeletal structure of the head. The skull is a bony framework of the head, consisting of 22 bones. The skull forms the frontmost portion of the axial skeleton and is a product of cephalization and vesicular enlargement of the brain, with several special senses structures such as the eyes,. There are 29 bones (including the hyoid and. It is divided into two main parts: The. Complete guide for students to explore structure & function of the human skull. There are 29 bones (including the hyoid and. The skull forms the frontmost portion of the axial skeleton and is a product of cephalization and vesicular enlargement of the brain, with several special senses structures such as the eyes,. The skull is a bony framework of the. Your skull is the part of your skeleton that holds and protects your brain. The cranium, which encases the brain, and the facial skeleton, which supports. It is subdivided into the facial bones and the cranium, or cranial vault (figure 7.3.1). Skull, skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, composed of bones or cartilage, which form a unit that protects. Commonly expresses figurative death, e.g., dying from extreme laughter, frustration, or affection. It is comprised of many bones, formed by intramembranous ossification, which are. There are 29 bones (including the hyoid and. Your skull is the part of your skeleton that holds and protects your brain. It is subdivided into the facial bones and the cranium, or cranial vault (figure. Learn a skull anatomy with parts, names & detailed diagram. The skull is a bony framework of the head, consisting of 22 bones. Your skull is the part of your skeleton that holds and protects your brain. There are 29 bones (including the hyoid and. The skull is a bony structure that supports the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. It is divided into two main parts: It is comprised of many bones, formed by intramembranous ossification, which are. Commonly expresses figurative death, e.g., dying from extreme laughter, frustration, or affection. Complete guide for students to explore structure & function of the human skull. The skull forms the frontmost portion of the axial skeleton and is a product of cephalization and vesicular enlargement of the brain, with several special senses structures such as the eyes,. Skull, skeletal framework of the head of vertebrates, composed of bones or cartilage, which form a unit that protects the brain and some sense organs. It also holds or supports several of your main sensory organs, like your eyes, ears,. It is subdivided into the facial bones and the cranium, or cranial vault (figure 7.3.1).Wildlife Skull Identification Forensic Set KIMSeattle
Rodent Skull Identification Chart
Rodent Skull Identification Chart
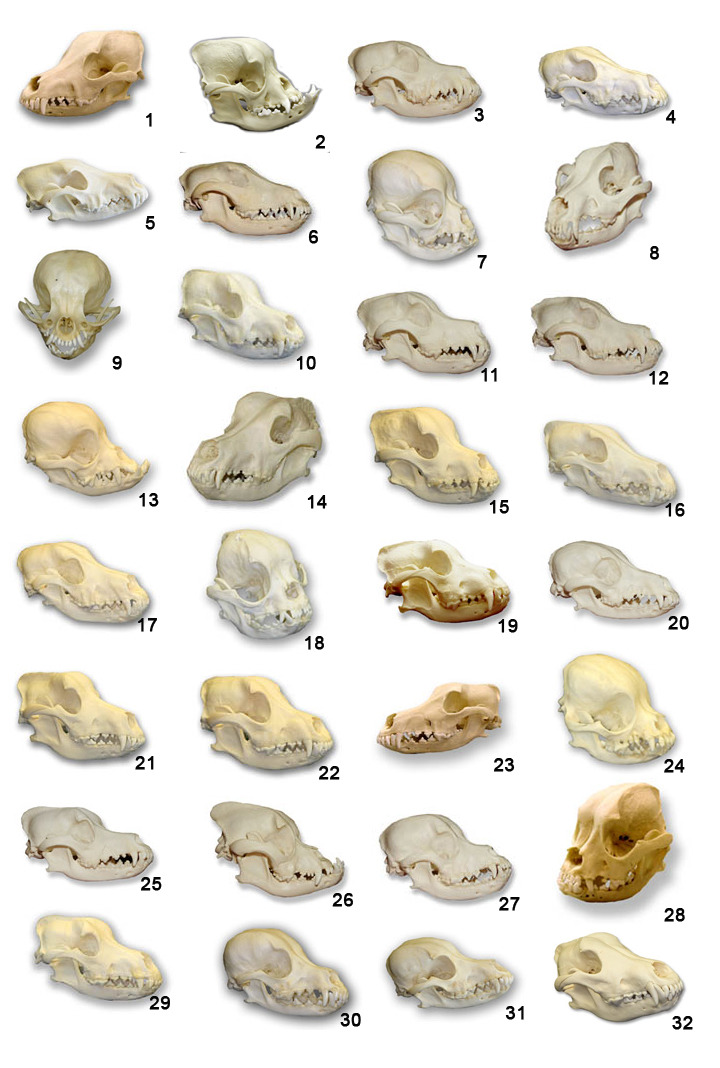
For my scientific illustration class, I made an identification guide to the common mammal skulls
Rodent Skull Identification Chart
Animal Skull Identification Guide Waking Up Wild Waking Up Wild
Rodent Skull Identification Chart
Rodent Skull Identification Chart Ponasa
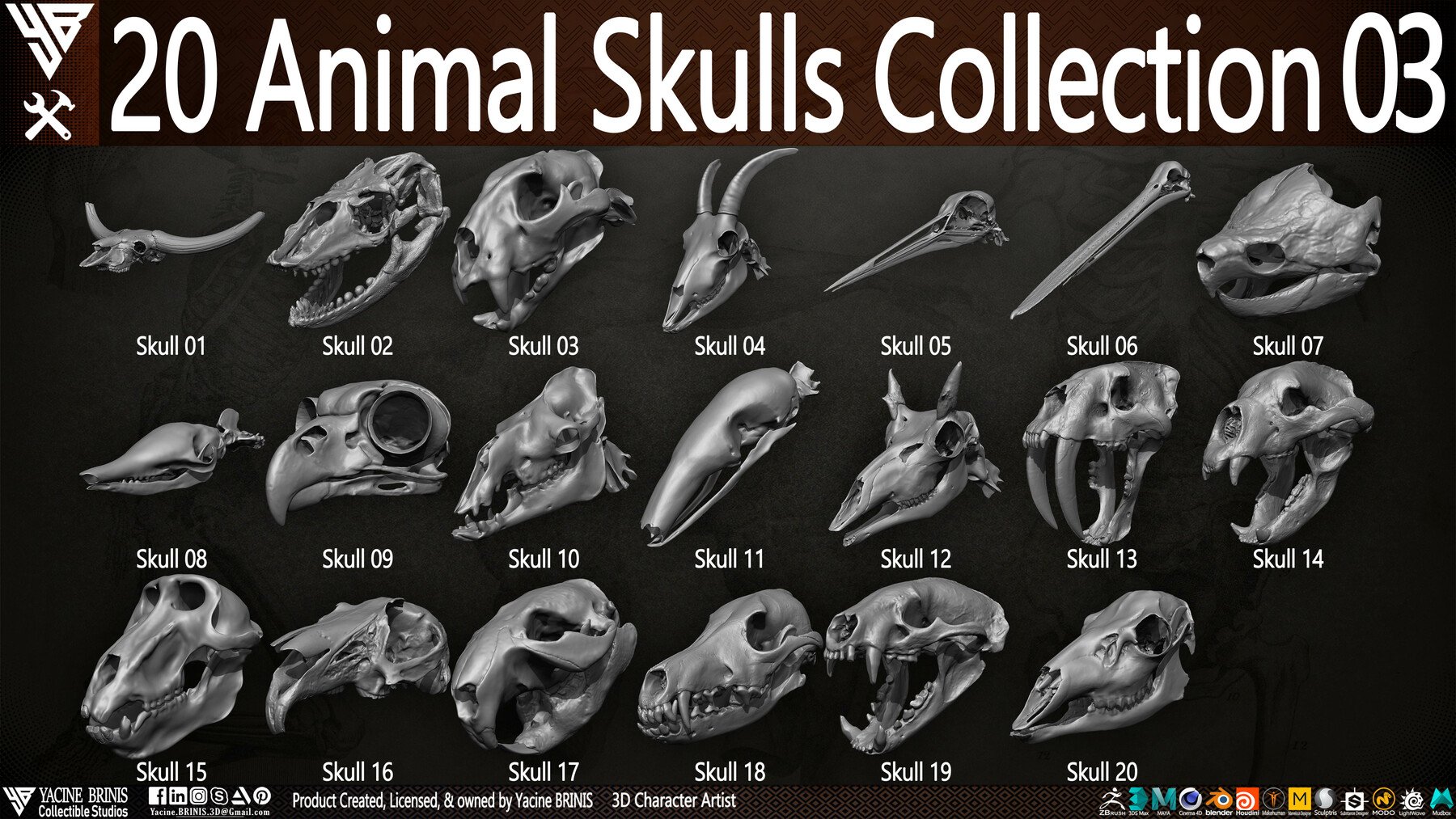
ArtStation 20 Animal Skulls Collection 03 Resources
Rodent Skull Identification Chart
The Skull Is One Of The Most Vital Bony Structures Of The Human Body, As It Houses And Protects The Most Important Organs, Including The Brain.
The Cranium, Which Encases The Brain, And The Facial Skeleton, Which Supports.
The Skull Is The Skeletal Structure Of The Head That Supports The Face And Protects The Brain.
The Human Skull Consists Of 22 Bones (Or 29, Including The Inner Ear Bones And Hyoid Bone) Which Are Mostly Connected Together By Ossified Joints, So Called Sutures.
Related Post: