Viscosity Chart For Oil
Viscosity Chart For Oil - Viscosity is a physical quantity that describes a fluid’s resistance to flow. Viscosity denotes opposition to flow. Viscosity is defined as the measure of a fluid's resistance to fluid flow under an applied force. It is a property that resists the relative displacement of the different layers of the fluid. Formally, viscosity is the ratio of shearing stress to velocity gradient. You’ll also explore the reasons why viscosity is important. Viscosity is a measure of the resistance to flow that a liquid exhibits because of the internal friction that occurs between the different layers of the fluid. The majority of fluids have. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid (liquid or gas) to a change in shape or movement of neighbouring portions relative to one another. A fluid with a high viscosity, such as honey, flows as a slower rate than a less viscous fluid, such as water. Viscosity is defined as the measure of a fluid's resistance to fluid flow under an applied force. The violet fluid at the bottom has a higher viscosity than the clear one above viscosity is a physical property of fluids. For a fluid in motion, the viscosity describes the internal friction. The majority of fluids have. Viscosity denotes opposition to flow. Formally, viscosity is the ratio of shearing stress to velocity gradient. Informally, viscosity is the quantity that describes a fluid's resistance to flow. It shows resistance to flow. Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid (liquid or gas) to a change in shape or movement of neighbouring portions relative to one another. The majority of fluids have. The violet fluid at the bottom has a higher viscosity than the clear one above viscosity is a physical property of fluids. Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid (liquid or gas) to a change in shape or movement of neighbouring portions relative to one another. Viscosity is a physical quantity that describes a fluid’s. Viscosity denotes opposition to flow. Formally, viscosity is the ratio of shearing stress to velocity gradient. The opposite of viscosity is fluidity which measures the ease of flow while liquids. In this article, you will learn what viscosity is, how it is measured, and the viscosity equation of a fluid. Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid (liquid or gas). Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Viscosity can be not only a fluid’s resistance to flow but also a gas’ resistance to flow, change shape or movement. [1] viscosity quantifies the internal. A fluid with a high viscosity, such as honey, flows as a slower rate than a less viscous fluid,. Formally, viscosity is the ratio of shearing stress to velocity gradient. By definition, viscosity is a fluid’s resistance to flow or deformation. Informally, viscosity is the quantity that describes a fluid's resistance to flow. The majority of fluids have. Viscosity is a measure of the resistance to flow that a liquid exhibits because of the internal friction that occurs between. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. It shows resistance to flow. The majority of fluids have. Viscosity is a physical quantity that describes a fluid’s resistance to flow. By definition, viscosity is a fluid’s resistance to flow or deformation. In this article, you will learn what viscosity is, how it is measured, and the viscosity equation of a fluid. Viscosity is a measure of the resistance to flow that a liquid exhibits because of the internal friction that occurs between the different layers of the fluid. A fluid with a high viscosity, such as honey, flows as a slower. Informally, viscosity is the quantity that describes a fluid's resistance to flow. In this article, you will learn what viscosity is, how it is measured, and the viscosity equation of a fluid. Formally, viscosity is the ratio of shearing stress to velocity gradient. Viscosity is a measure of the resistance to flow that a liquid exhibits because of the internal. [1] in a simple example,. By definition, viscosity is a fluid’s resistance to flow or deformation. A fluid with a high viscosity, such as honey, flows as a slower rate than a less viscous fluid, such as water. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. In this article, you will learn what. It is a property that resists the relative displacement of the different layers of the fluid. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Viscosity denotes opposition to flow. By definition, viscosity is a fluid’s resistance to flow or deformation. You’ll also explore the reasons why viscosity is important. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. A fluid with a high viscosity, such as honey, flows as a slower rate than a less viscous fluid, such as water. [1] in a simple example,. The majority of fluids have. Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid (liquid or gas) to a change. Formally, viscosity is the ratio of shearing stress to velocity gradient. In this article, you will learn what viscosity is, how it is measured, and the viscosity equation of a fluid. [1] viscosity quantifies the internal. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. By definition, viscosity is a fluid’s resistance to flow or deformation. You’ll also explore the reasons why viscosity is important. Viscosity is a physical quantity that describes a fluid’s resistance to flow. Informally, viscosity is the quantity that describes a fluid's resistance to flow. The majority of fluids have. Viscosity can be not only a fluid’s resistance to flow but also a gas’ resistance to flow, change shape or movement. Viscosity denotes opposition to flow. Viscosity is defined as the measure of a fluid's resistance to fluid flow under an applied force. For a fluid in motion, the viscosity describes the internal friction. It shows resistance to flow. Viscosity is a measure of the resistance to flow that a liquid exhibits because of the internal friction that occurs between the different layers of the fluid. The opposite of viscosity is fluidity which measures the ease of flow while liquids.Understanding the Viscosity Grade Chart
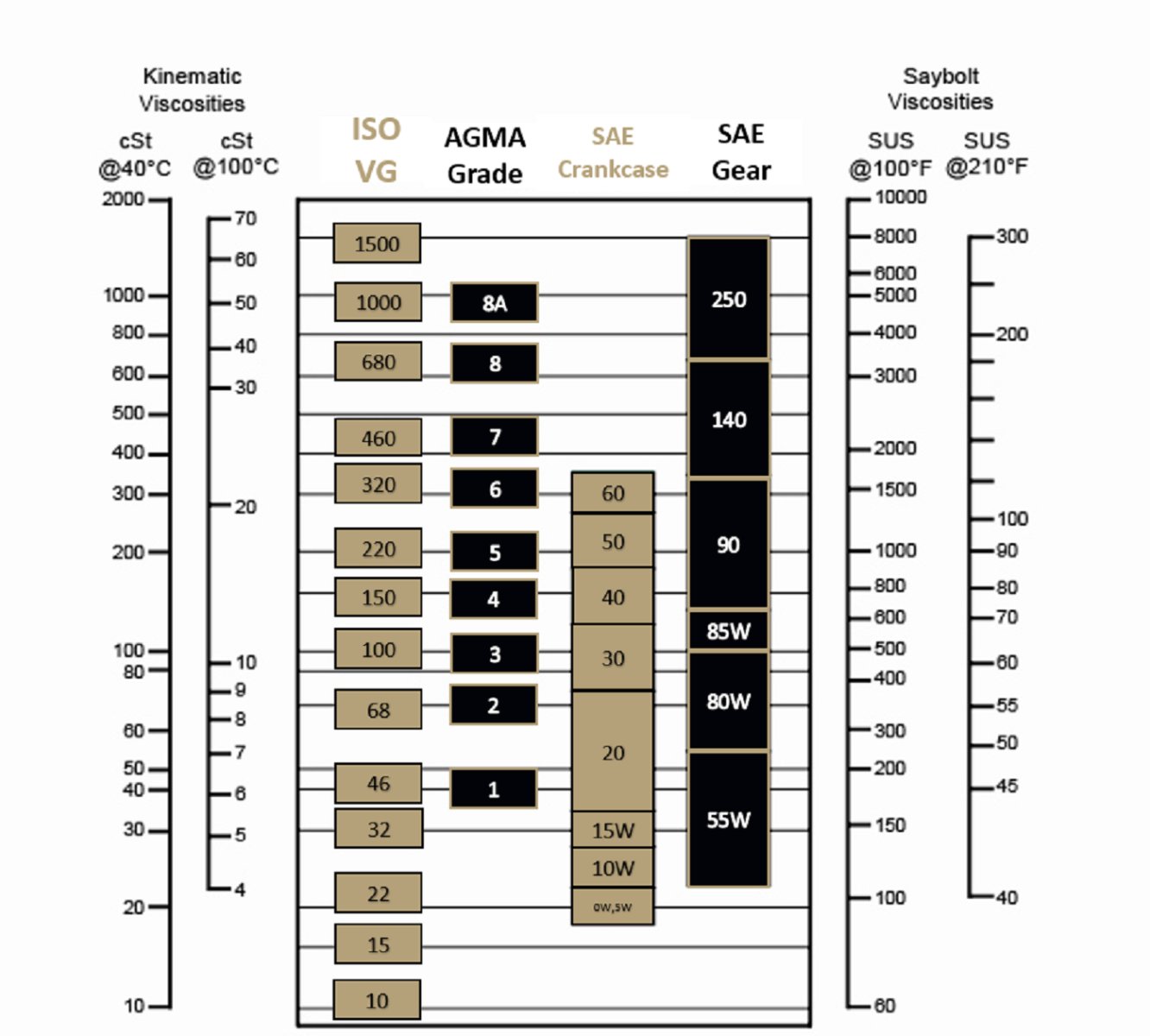
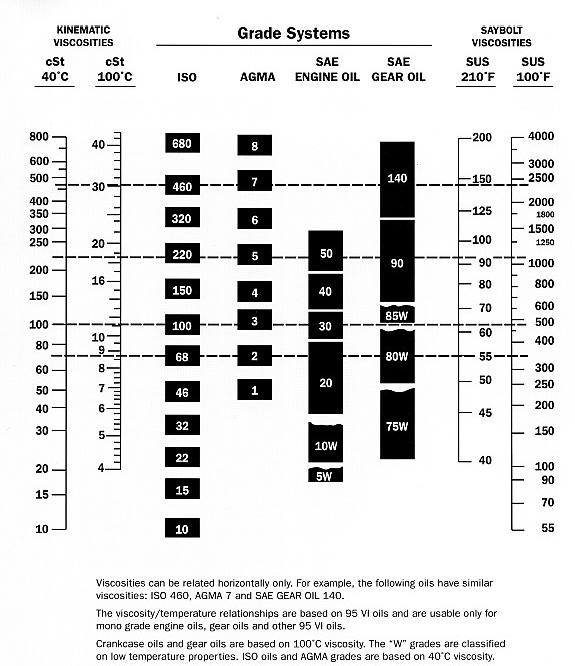
Oil Viscosity Comparison Chart ISO VG, AGMA, SAE Gear, SAE
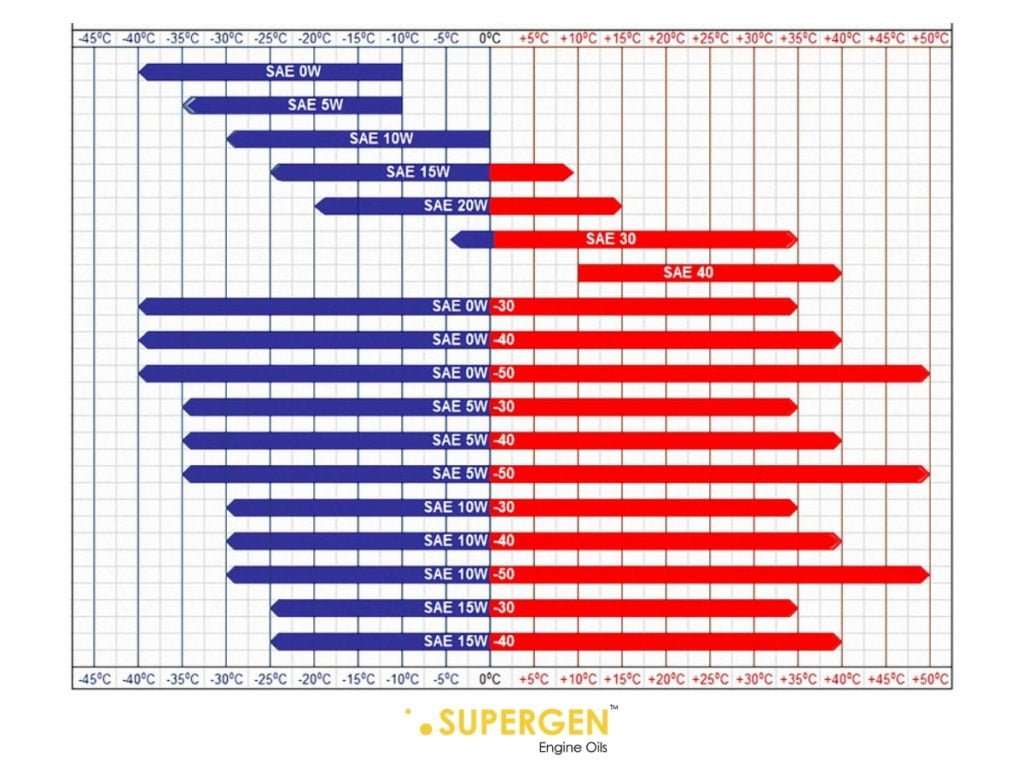
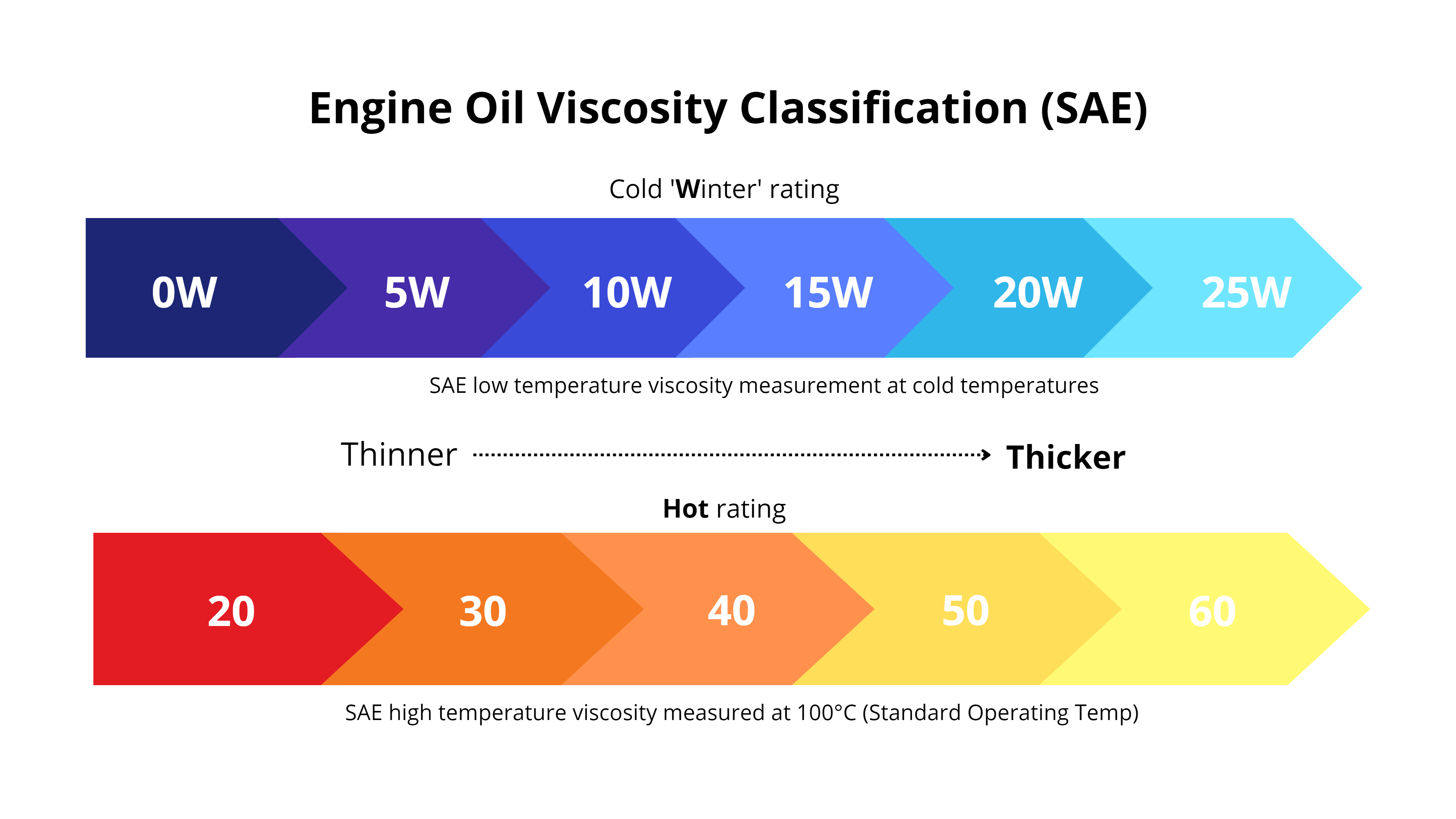
WHAT IS THE VISCOSITY GRADE OF ENGINE OIL? Supergen Engine Oils
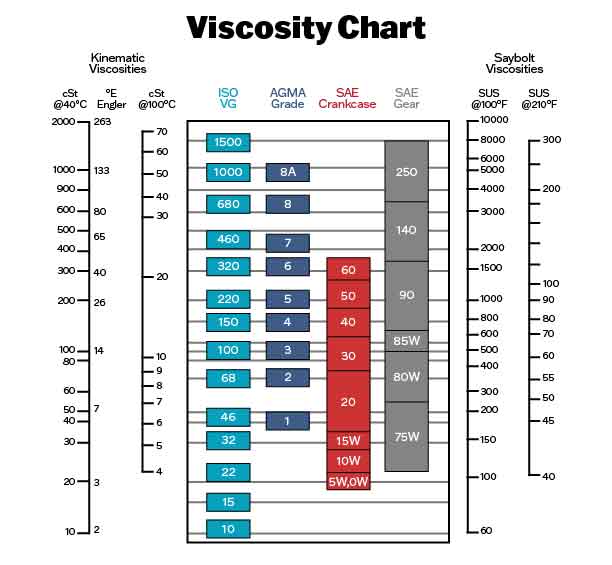
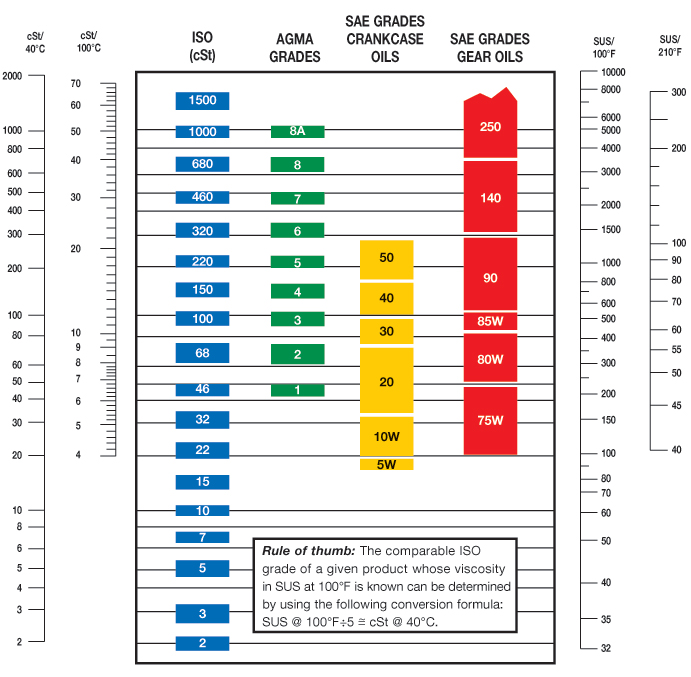
Oil Viscosity Chart Guide to Selecting the Right Oil
How to Choose An Oil Oil Viscosity Chart
Understanding a Viscosity Chart 49 North Lubricants
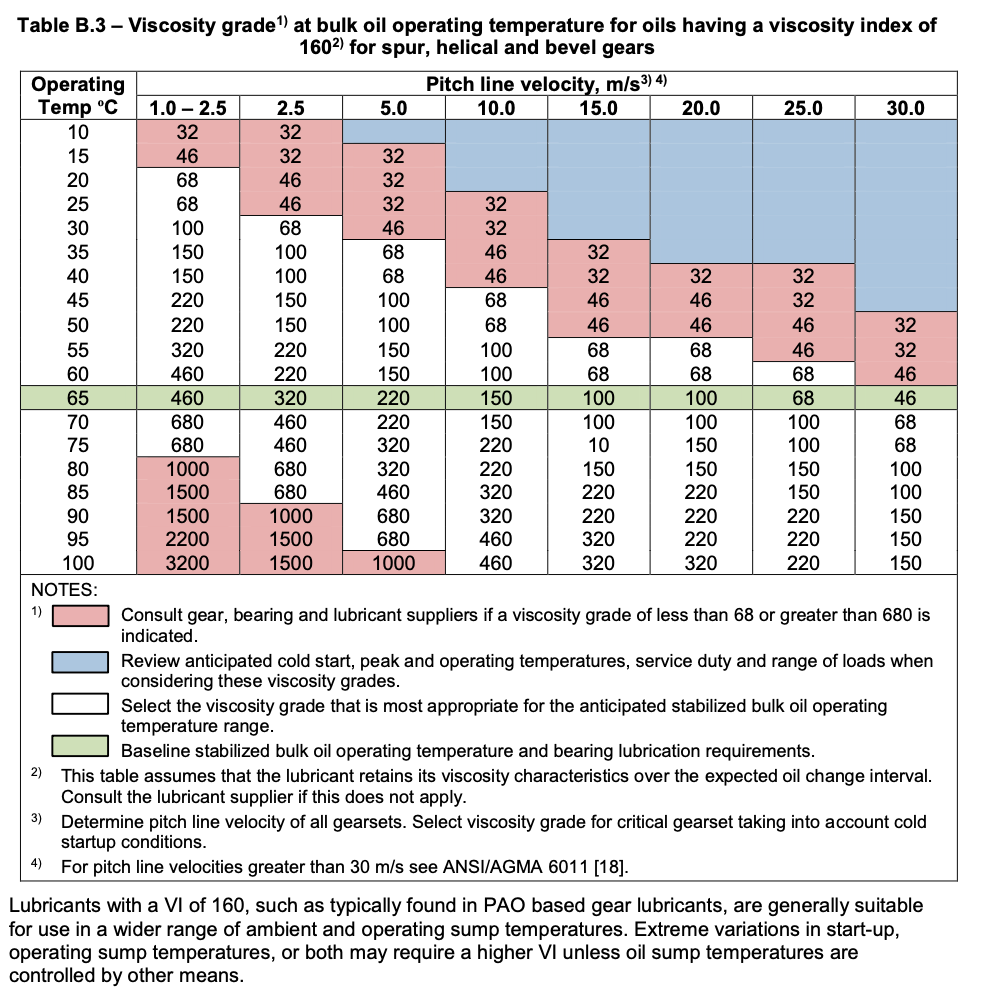
Viscosity Charts Bob is the Oil Guy
Oil Viscosity Chart Guide to Selecting the Right Oil
Oil Viscosity Numbers Explained
Understanding The Viscosity Grade Chart
The Violet Fluid At The Bottom Has A Higher Viscosity Than The Clear One Above Viscosity Is A Physical Property Of Fluids.
A Fluid With A High Viscosity, Such As Honey, Flows As A Slower Rate Than A Less Viscous Fluid, Such As Water.
It Is A Property That Resists The Relative Displacement Of The Different Layers Of The Fluid.
Viscosity Is The Resistance Of A Fluid (Liquid Or Gas) To A Change In Shape Or Movement Of Neighbouring Portions Relative To One Another.
Related Post: