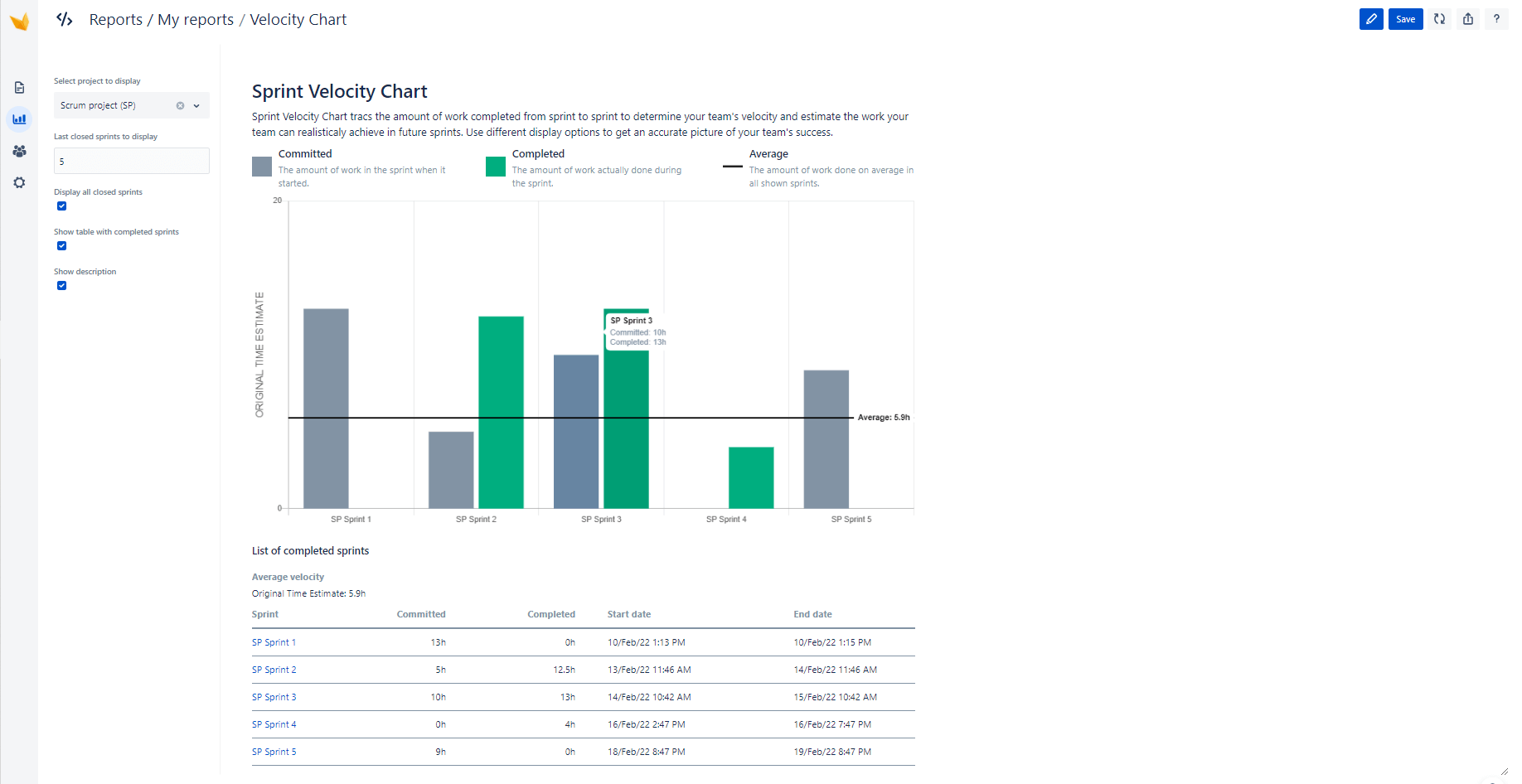
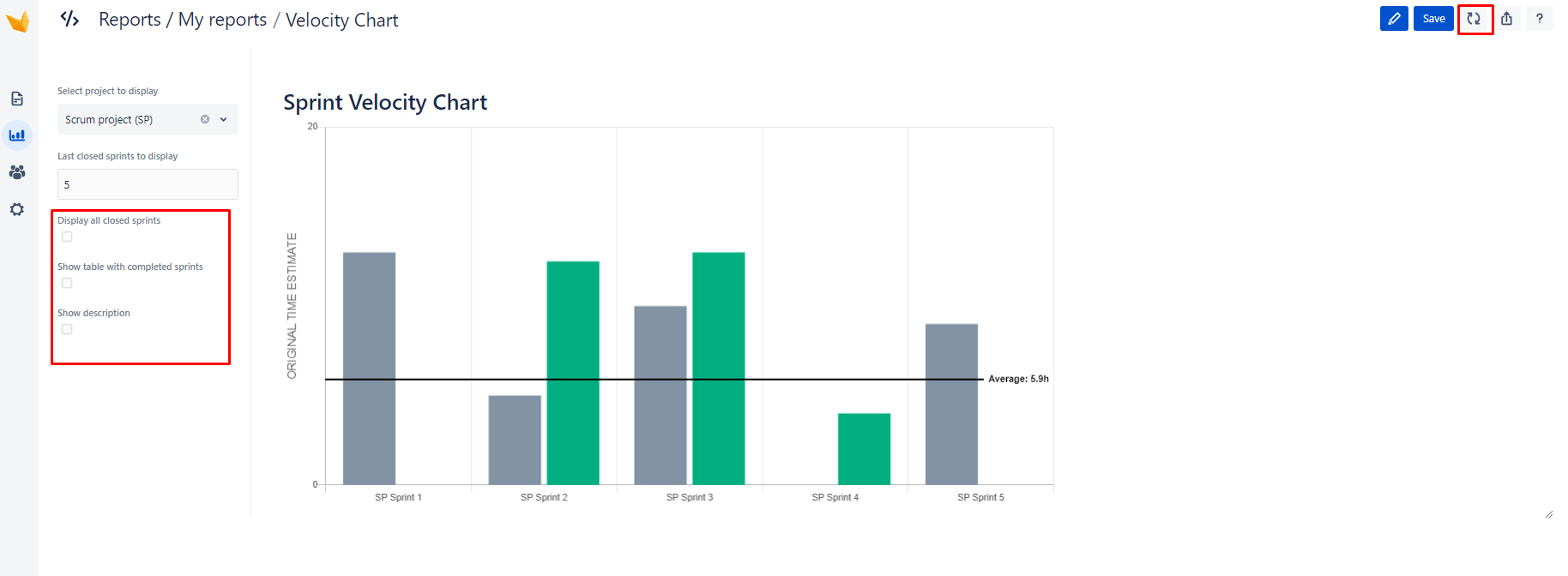
Velocity Chart Jira
Velocity Chart Jira - Velocity is the speed at which an object is moving. The integral will produce a function of velocity versus time, so the constant would be added or subtracted from the function of velocity at time = zero to account for the initial velocity. I thought velocity was always a vector quantity, one with both magnitude and direction. That does not mean that the viscosity is a function of velocity. The viscous force within a fluid will depend on the velocity gradient (aka shear rate) within the fluid. I am not sure even how to approach this. When it came to the suvat equations, where v = final velocity, and u = initial velocity,. You can calculate the amount of torque required to accelerate the object, say from rest to a certain angular velocity. Your question is a bit unclear. I am trying to work with the simplified bernoulli equation to determine how to convert a drop in flow velocity across a stenosis (narrowing) into a change in hemodynamic pressure. An increase in the height from which an object is dropped positively correlates with the final velocity of the object as it falls. The viscous force within a fluid will depend on the velocity gradient (aka shear rate) within the fluid. If you want to determine what. I am trying to work with the simplified bernoulli equation to determine how to convert a drop in flow velocity across a stenosis (narrowing) into a change in hemodynamic pressure. You can calculate the amount of torque required to accelerate the object, say from rest to a certain angular velocity. It can also be thought of as the speed of a moving object divided by the time of travel. How does the velocity of the escaping gas relate to the diameter of the hole? When it came to the suvat equations, where v = final velocity, and u = initial velocity,. Velocity is the speed at which an object is moving. The integral will produce a function of velocity versus time, so the constant would be added or subtracted from the function of velocity at time = zero to account for the initial velocity. When it came to the suvat equations, where v = final velocity, and u = initial velocity,. That does not mean that the viscosity is a function of velocity. I am trying to work with the simplified bernoulli equation to determine how to convert a drop in flow velocity across a stenosis (narrowing) into a change in hemodynamic pressure. How. The viscous force within a fluid will depend on the velocity gradient (aka shear rate) within the fluid. It can also be thought of as the speed of a moving object divided by the time of travel. My first impulse is to apply bernoulli's principal. To do this we work out the area of the nozzle and. You can calculate. When it came to the suvat equations, where v = final velocity, and u = initial velocity,. Calculating nozzle flow rate to work out the flow rate of water from a nozzle we need to work out the volume in a given period of time. Velocity is the speed at which an object is moving. The viscous force within a. When it came to the suvat equations, where v = final velocity, and u = initial velocity,. I was going through periodic motion chapter of my book and came across an equation while defining the relation between time period of on oscillating particle and force. My first impulse is to apply bernoulli's principal. To do this we work out the. The viscous force within a fluid will depend on the velocity gradient (aka shear rate) within the fluid. You can calculate the amount of torque required to accelerate the object, say from rest to a certain angular velocity. It has more time to fall, so it will hit at a greater speed. It can also be thought of as the. I am trying to work with the simplified bernoulli equation to determine how to convert a drop in flow velocity across a stenosis (narrowing) into a change in hemodynamic pressure. Your question is a bit unclear. When it came to the suvat equations, where v = final velocity, and u = initial velocity,. Velocity is the speed at which an. I was going through periodic motion chapter of my book and came across an equation while defining the relation between time period of on oscillating particle and force. I thought velocity was always a vector quantity, one with both magnitude and direction. That does not mean that the viscosity is a function of velocity. I am not sure even how. Velocity is the speed at which an object is moving. An increase in the height from which an object is dropped positively correlates with the final velocity of the object as it falls. That does not mean that the viscosity is a function of velocity. When it came to the suvat equations, where v = final velocity, and u =. It has more time to fall, so it will hit at a greater speed. Calculating nozzle flow rate to work out the flow rate of water from a nozzle we need to work out the volume in a given period of time. If you want to determine what. It can also be thought of as the speed of a moving. To do this we work out the area of the nozzle and. In this case, it is the speed of a body. It can also be thought of as the speed of a moving object divided by the time of travel. It has more time to fall, so it will hit at a greater speed. An increase in the height. If you want to determine what. I am not sure even how to approach this. How does the velocity of the escaping gas relate to the diameter of the hole? The integral will produce a function of velocity versus time, so the constant would be added or subtracted from the function of velocity at time = zero to account for the initial velocity. Calculating nozzle flow rate to work out the flow rate of water from a nozzle we need to work out the volume in a given period of time. It has more time to fall, so it will hit at a greater speed. An increase in the height from which an object is dropped positively correlates with the final velocity of the object as it falls. I am trying to work with the simplified bernoulli equation to determine how to convert a drop in flow velocity across a stenosis (narrowing) into a change in hemodynamic pressure. To do this we work out the area of the nozzle and. My first impulse is to apply bernoulli's principal. I was going through periodic motion chapter of my book and came across an equation while defining the relation between time period of on oscillating particle and force. You can calculate the amount of torque required to accelerate the object, say from rest to a certain angular velocity. Velocity is the speed at which an object is moving. It can also be thought of as the speed of a moving object divided by the time of travel. That does not mean that the viscosity is a function of velocity. Your question is a bit unclear.Create a New Sprint Manage it in JIRA Tech Agilist
Velocity Chart Template
How to perform Sprint Planning with Jira Part 2 Using Story Points, Velocity Pros and Cons
Velocity Charts in Jira for better sprint planning Actonic Unfolding your potential
How to Increase Confidence in Sprint Planning with Jira Velocity Charts Reports for Jira
Sprint Management with Jira Estimating Your Velocity Valiantys Federal
Velocity Charts in Jira for better sprint planning Actonic Unfolding your potential
Jira Filter Velocity Chart at Catherine Dorsey blog
How To Add Velocity Chart In Jira Dashboard Portal.posgradount.edu.pe
eazyBI Sprint Velocity Chart jira atlassian descript YouTube
The Viscous Force Within A Fluid Will Depend On The Velocity Gradient (Aka Shear Rate) Within The Fluid.
When It Came To The Suvat Equations, Where V = Final Velocity, And U = Initial Velocity,.
I Thought Velocity Was Always A Vector Quantity, One With Both Magnitude And Direction.
In This Case, It Is The Speed Of A Body.
Related Post: