Shape Charts
Shape Charts - What numpy calls the dimension is 2, in your case (ndim). 'nonetype' object has no attribute 'shape' occurs after passing an incorrect path to cv2.imread () because the path of image/video file is wrong or the. And you can get the (number of) dimensions of your array using. There's one good reason why to use shape in interactive work, instead of len (df): You can think of a placeholder in tensorflow as an operation specifying the shape and type of data that will be fed into the graph.placeholder x defines that an unspecified number of rows of. It's useful to know the usual numpy. In my android app, i have it like this: And i want to make this black. Trying out different filtering, i often need to know how many items remain. Your dimensions are called the shape, in numpy. It's useful to know the usual numpy. And i want to make this black. (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. 'nonetype' object has no attribute 'shape' occurs after passing an incorrect path to cv2.imread () because the path of image/video file is wrong or the. Shape is a tuple that gives you an indication of the number of dimensions in the array. So in your case, since the index value of y.shape[0] is 0, your are working along the first. What numpy calls the dimension is 2, in your case (ndim). 82 yourarray.shape or np.shape() or np.ma.shape() returns the shape of your ndarray as a tuple; Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get the shape in a tuple or list form? Trying out different filtering, i often need to know how many items remain. Shape of passed values is (x, ), indices imply (x, y) asked 11 years, 8 months ago modified 7 years, 4 months ago viewed 60k times Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get the shape in a tuple or list form? (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses. There's one good reason why to use shape in interactive work, instead of len (df): And i want to make this black. What numpy calls the dimension is 2, in your case (ndim). (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. Shape is a tuple that gives you an indication of the number of dimensions in. 'nonetype' object has no attribute 'shape' occurs after passing an incorrect path to cv2.imread () because the path of image/video file is wrong or the. (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. And you can get the (number of) dimensions of your array using. I already know how to set the opacity of the background. (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. 82 yourarray.shape or np.shape() or np.ma.shape() returns the shape of your ndarray as a tuple; I already know how to set the opacity of the background image but i need to set the opacity of my shape object. You can think of a placeholder in tensorflow as an. Trying out different filtering, i often need to know how many items remain. What numpy calls the dimension is 2, in your case (ndim). 82 yourarray.shape or np.shape() or np.ma.shape() returns the shape of your ndarray as a tuple; I already know how to set the opacity of the background image but i need to set the opacity of my. And you can get the (number of) dimensions of your array using. 82 yourarray.shape or np.shape() or np.ma.shape() returns the shape of your ndarray as a tuple; In my android app, i have it like this: Your dimensions are called the shape, in numpy. I already know how to set the opacity of the background image but i need to. You can think of a placeholder in tensorflow as an operation specifying the shape and type of data that will be fed into the graph.placeholder x defines that an unspecified number of rows of. Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get the shape in a tuple or list. In my android app, i have it like this: (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. And you can get the (number of) dimensions of your array using. Your dimensions are called the shape, in numpy. 'nonetype' object has no attribute 'shape' occurs after passing an incorrect path to cv2.imread () because the path of. In my android app, i have it like this: Trying out different filtering, i often need to know how many items remain. Shape of passed values is (x, ), indices imply (x, y) asked 11 years, 8 months ago modified 7 years, 4 months ago viewed 60k times (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d.. 82 yourarray.shape or np.shape() or np.ma.shape() returns the shape of your ndarray as a tuple; (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. It's useful to know the usual numpy. There's one good reason why to use shape in interactive work, instead of len (df): Your dimensions are called the shape, in numpy. (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. You can think of a placeholder in tensorflow as an operation specifying the shape and type of data that will be fed into the graph.placeholder x defines that an unspecified number of rows of. So in your case, since the index value of y.shape[0] is 0, your are working along the first. Your dimensions are called the shape, in numpy. And you can get the (number of) dimensions of your array using. 'nonetype' object has no attribute 'shape' occurs after passing an incorrect path to cv2.imread () because the path of image/video file is wrong or the. I already know how to set the opacity of the background image but i need to set the opacity of my shape object. There's one good reason why to use shape in interactive work, instead of len (df): Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get the shape in a tuple or list form? What numpy calls the dimension is 2, in your case (ndim). In my android app, i have it like this: Shape of passed values is (x, ), indices imply (x, y) asked 11 years, 8 months ago modified 7 years, 4 months ago viewed 60k times It's useful to know the usual numpy.Geometric Shapes Chart Printable
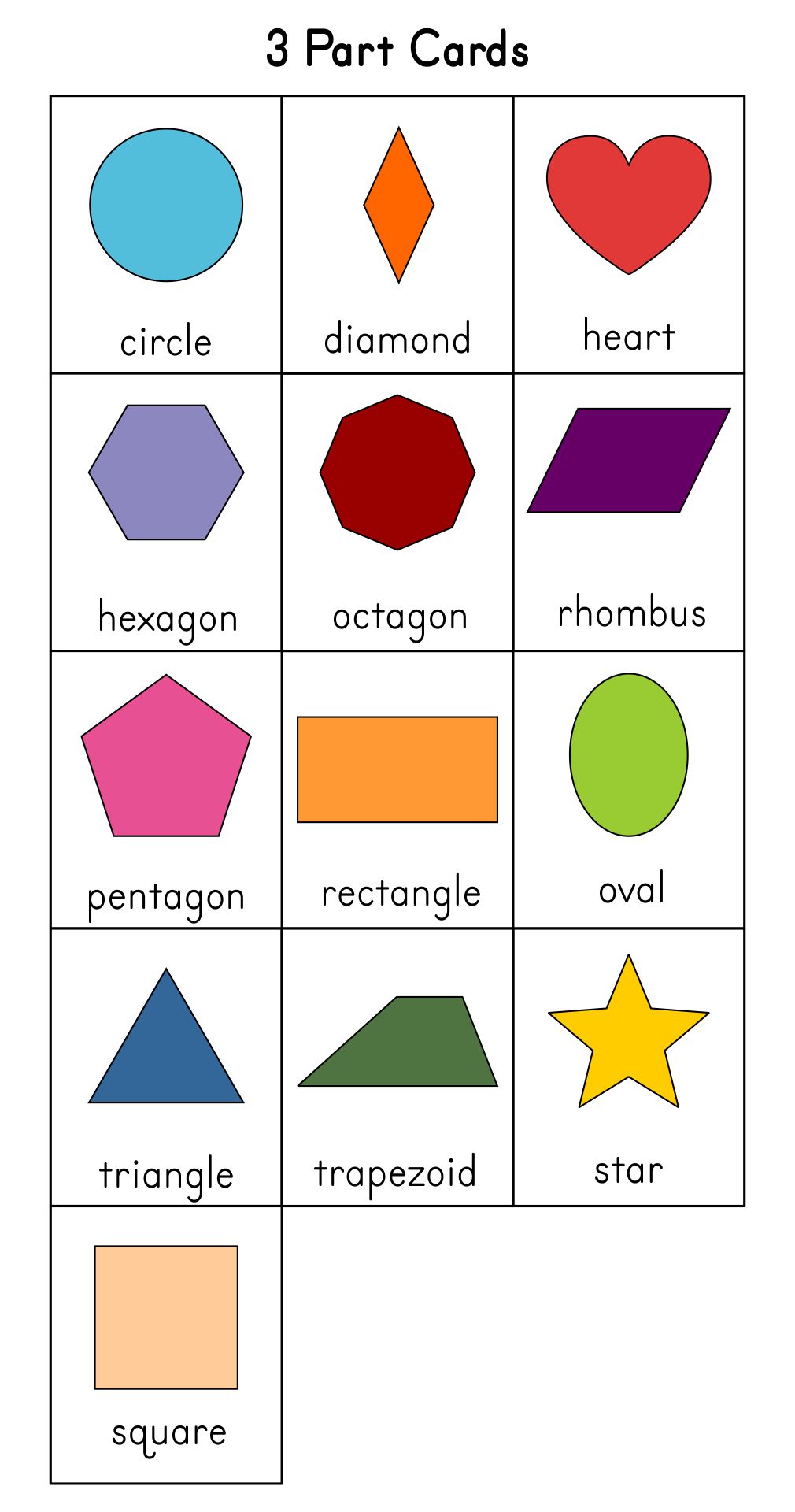
Printable Shapes Chart
Shapes Chart Printable
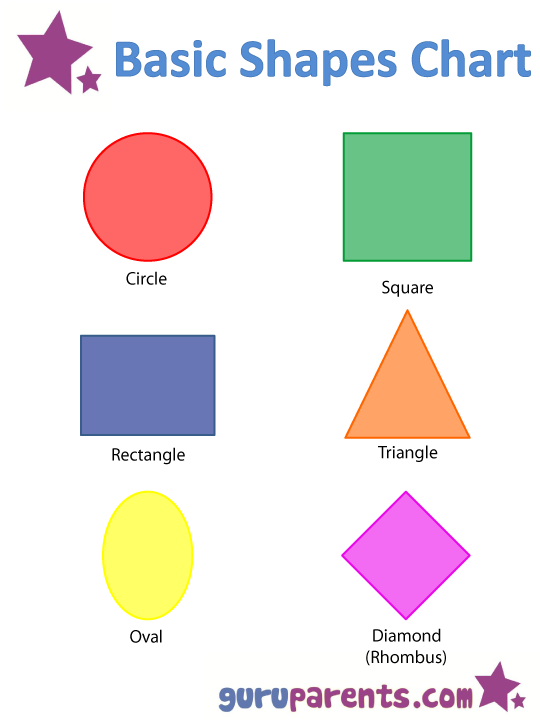
Shapes Chart guruparents
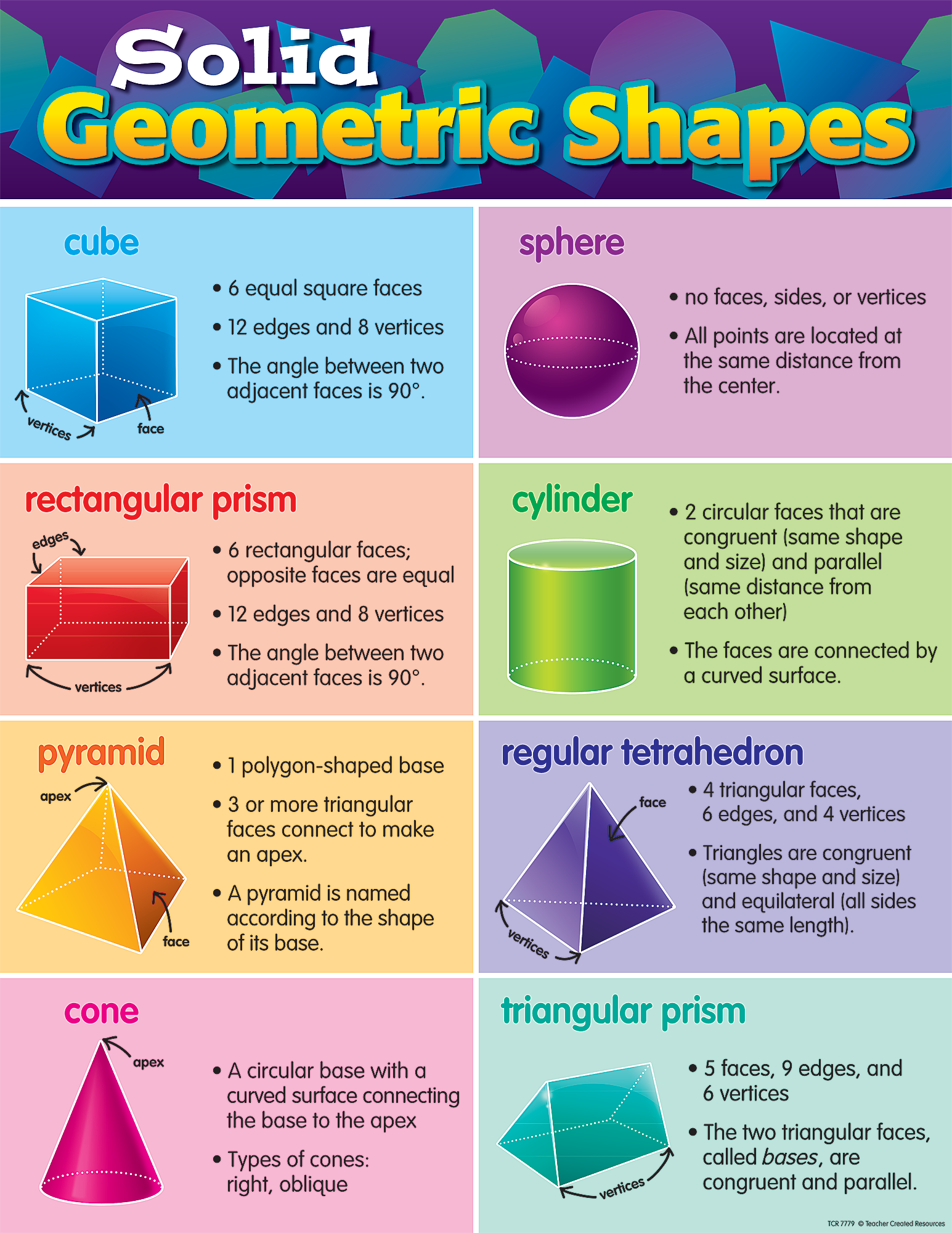
Solid Geometric Shapes Chart TCR7779 Teacher Created Resources
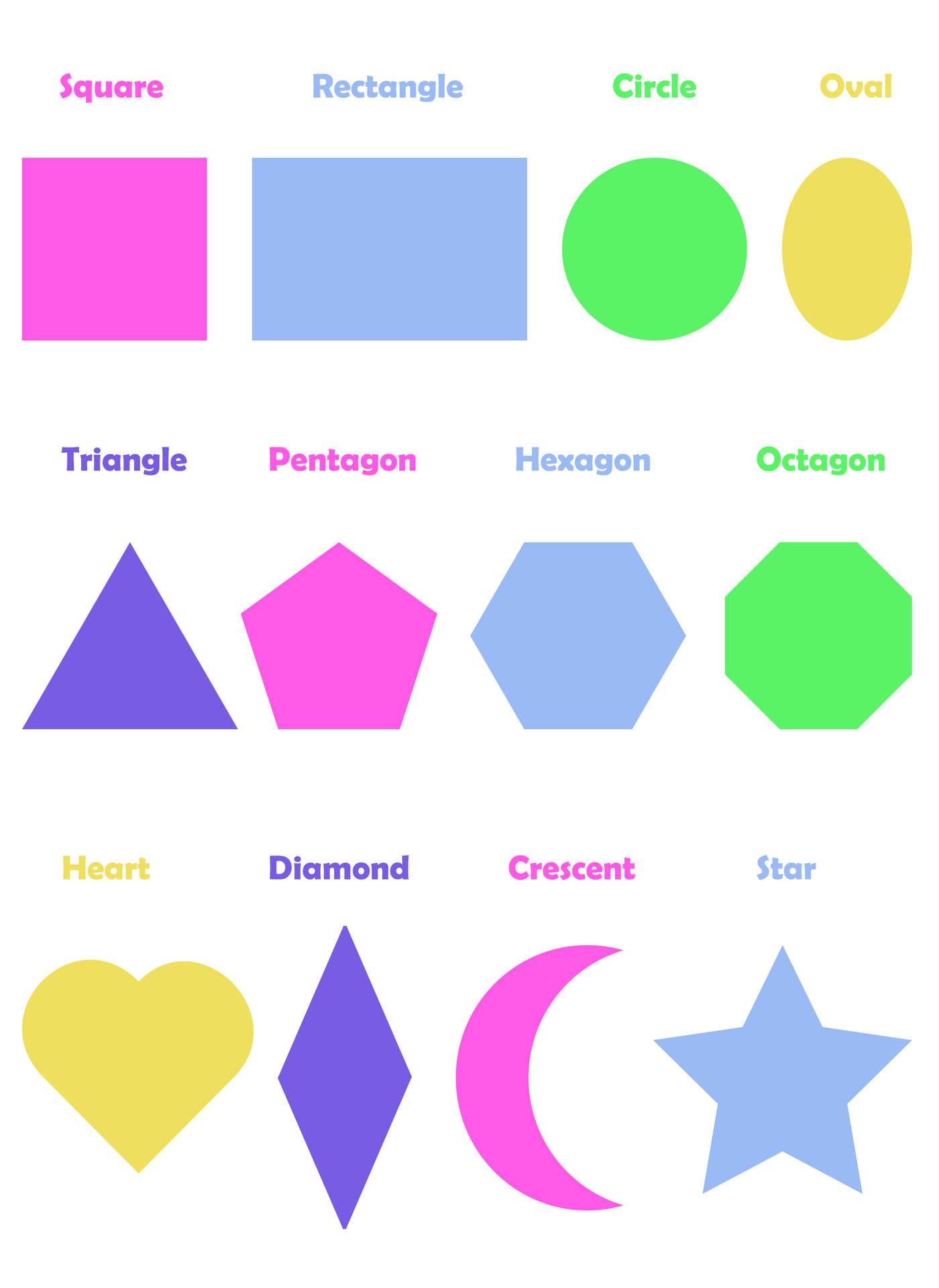
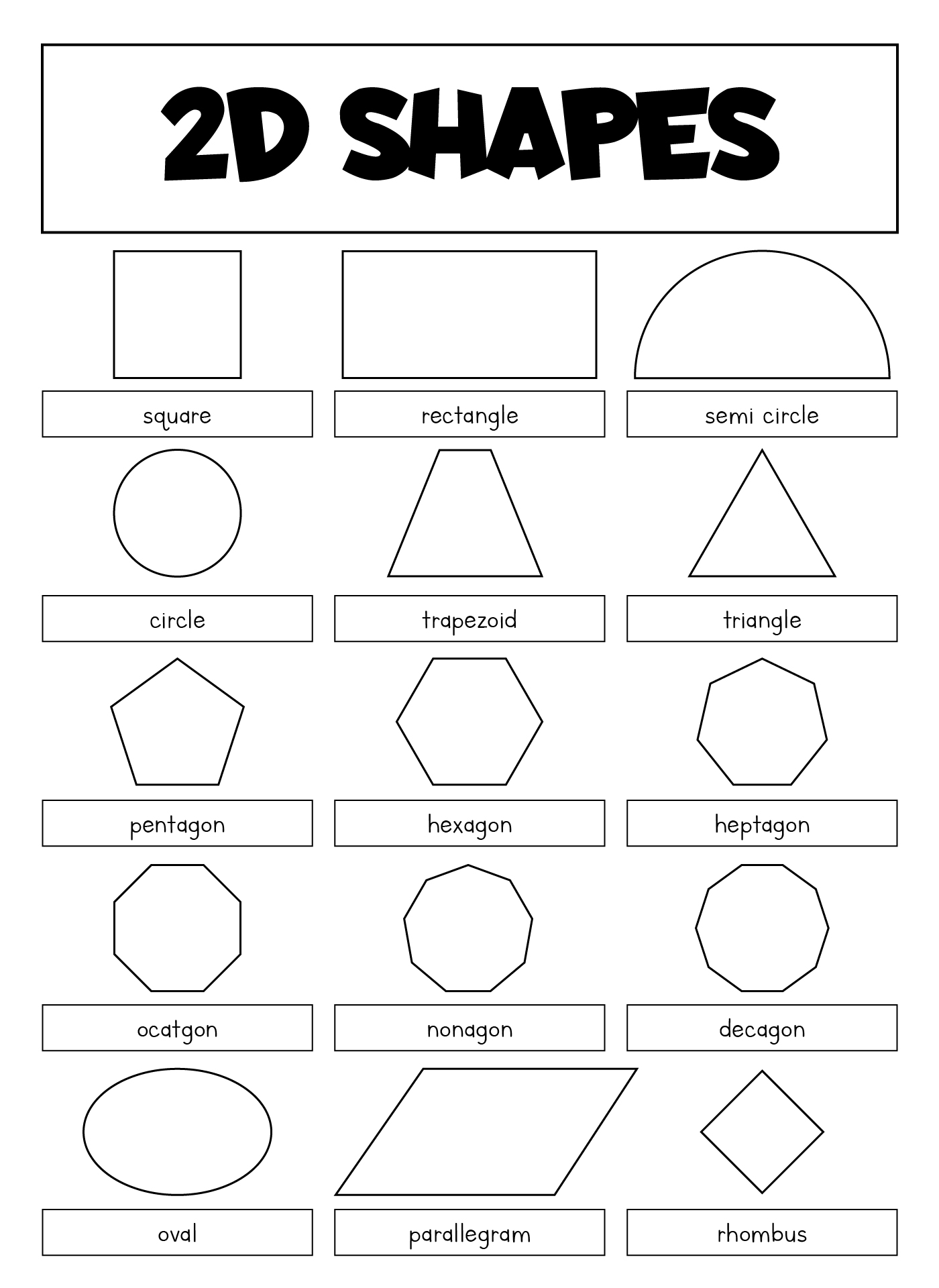
Shapes Chart 10 Free PDF Printables Printablee
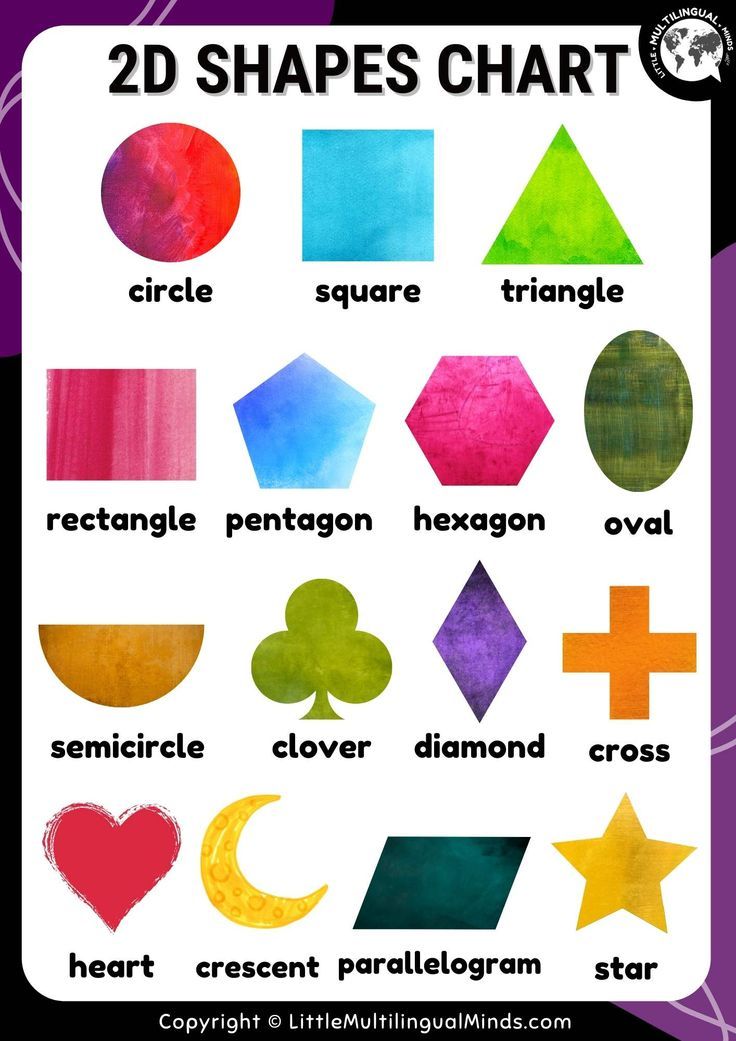
Printable Shapes Chart
Printable Shapes Chart
Shapes Chart 10 Free PDF Printables Printablee
Shapes Chart 10 Free PDF Printables Printablee
82 Yourarray.shape Or Np.shape() Or Np.ma.shape() Returns The Shape Of Your Ndarray As A Tuple;
And I Want To Make This Black.
Trying Out Different Filtering, I Often Need To Know How Many Items Remain.
Shape Is A Tuple That Gives You An Indication Of The Number Of Dimensions In The Array.
Related Post: