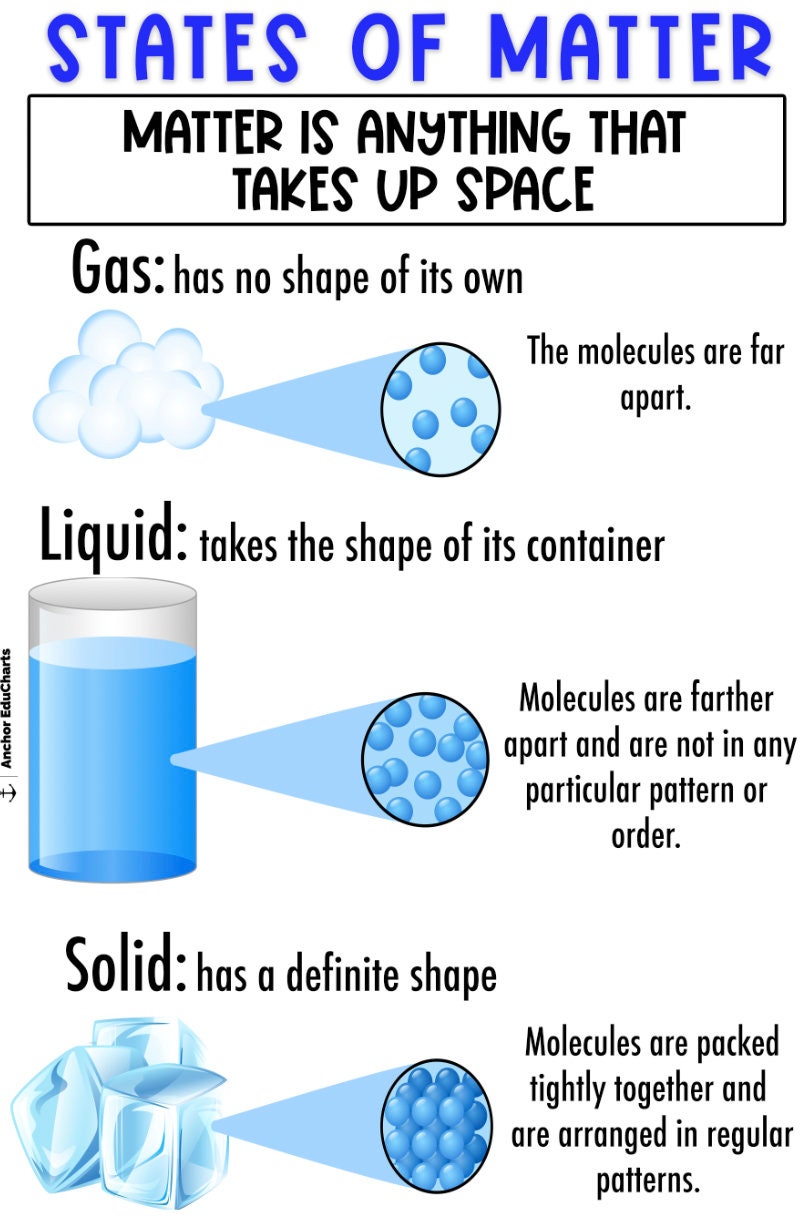
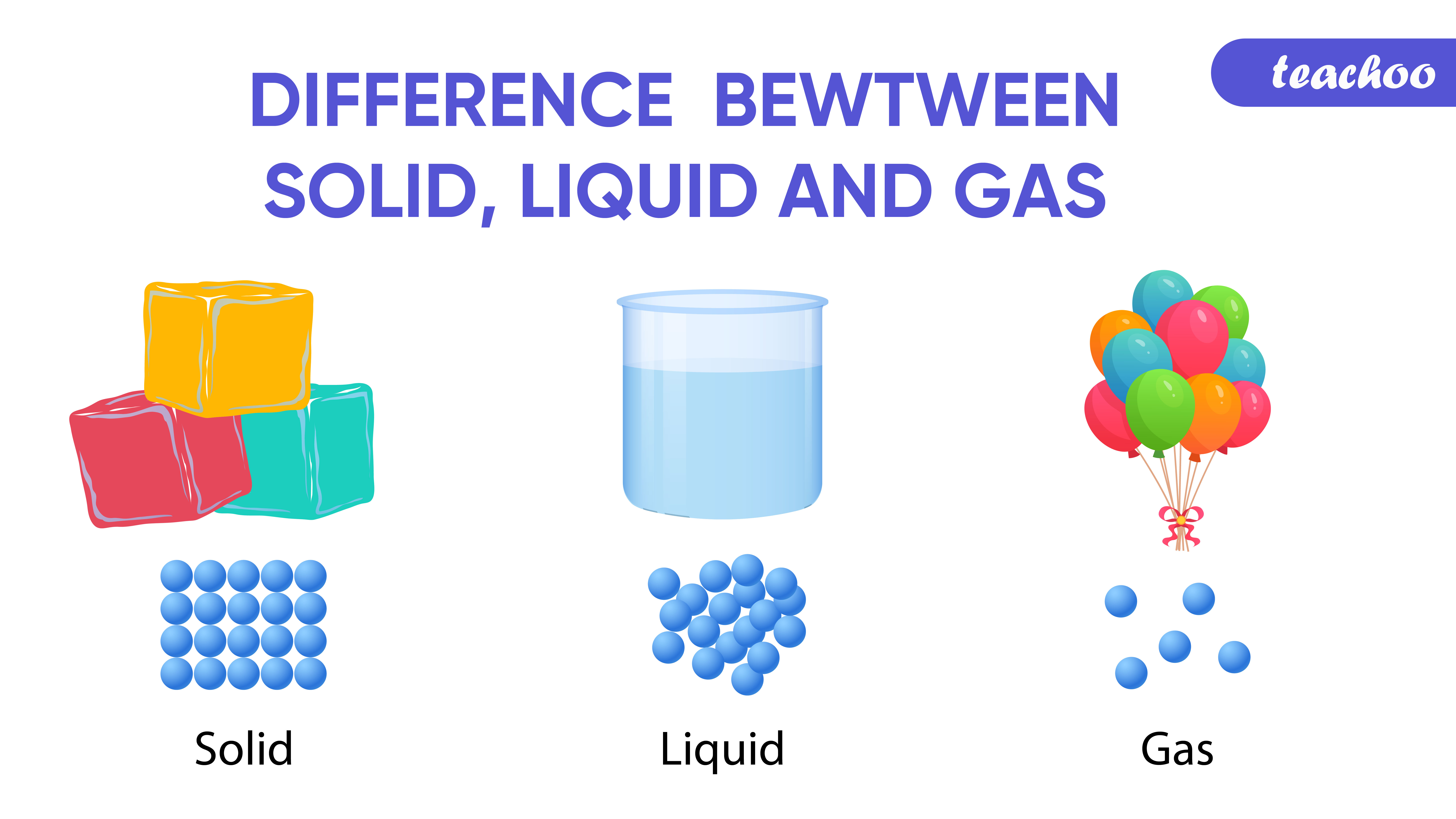
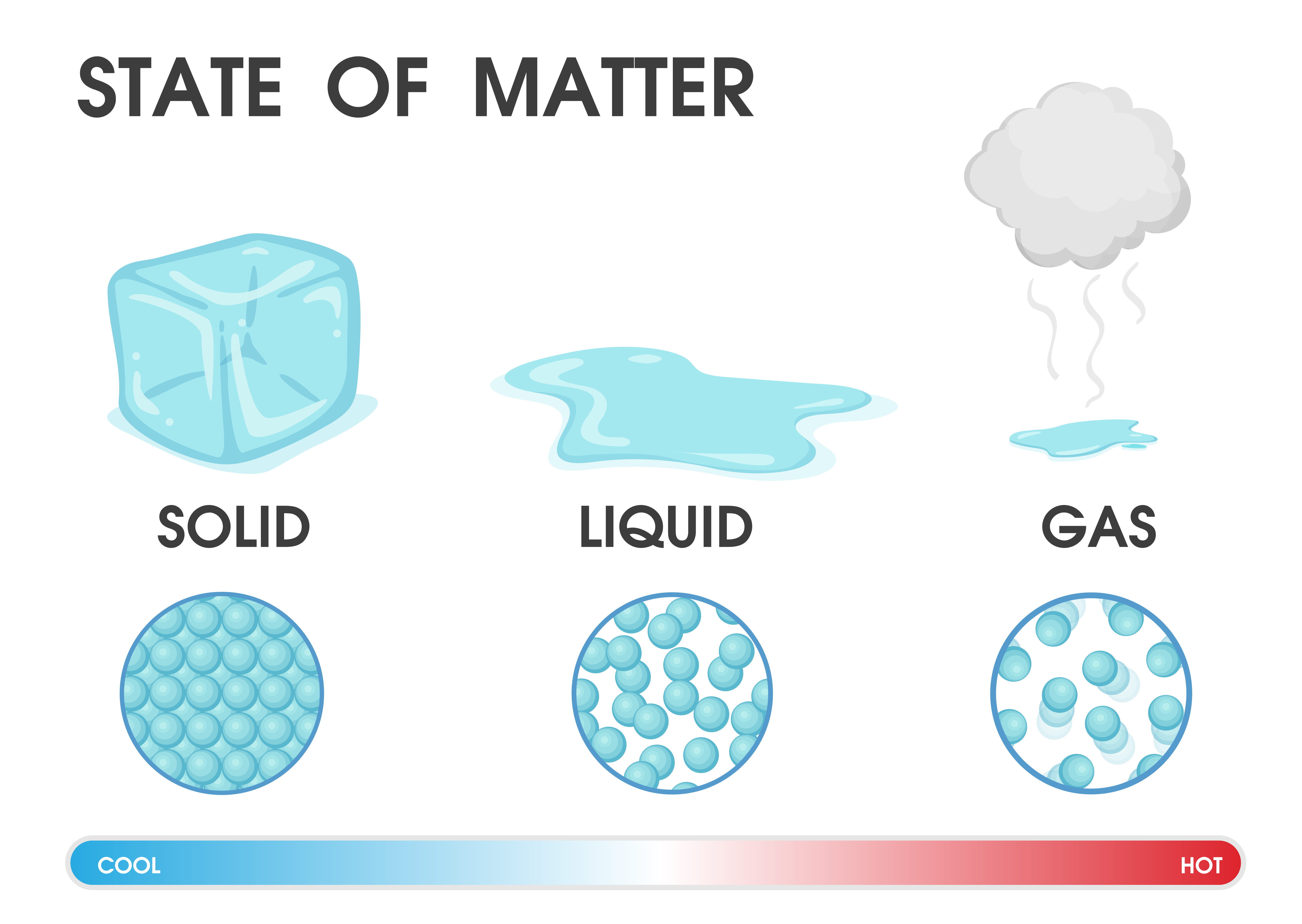
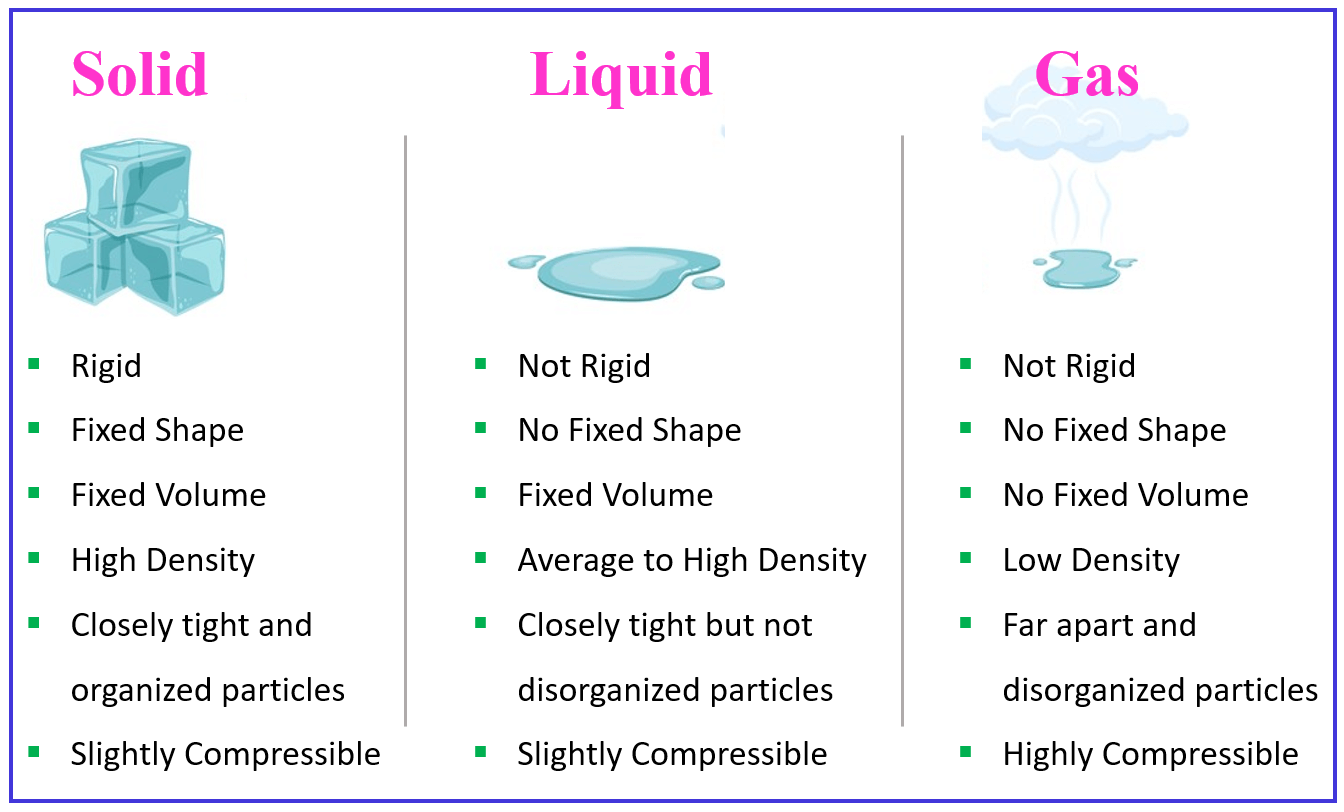
Liquid Gas Solid Chart
Liquid Gas Solid Chart - Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. It is characterized by its ability to retain almost a constant. Liquid, in physics, one of the three principal states of matter, intermediate between gas and crystalline solid. A liquid is a state of matter that flows freely and takes the shape of its container but maintains a constant volume. Unlike a solid, a liquid has no fixed shape, but instead has a characteristic readiness to flow and therefore takes on the shape of any container. A liquid represents one of the fundamental states of matter, characterized by particles that possess the ability to flow. In other words, a liquid takes the shape of its. A liquid is a state of matter that has a definite volume, but no fixed shape. A liquid is one of the three main states of matter, along with solids and gases. Unlike a gas, a liquid usually has a volume that. Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. The most obvious physical properties of a liquid are its retention of volume. Unlike a solid, a liquid has no fixed shape, but instead has a characteristic readiness to flow and therefore takes on the shape of any container. Water ceases to be a liquid when it is frozen or turned to steam. A liquid is one of the three main states of matter, along with solids and gases. Unlike a gas, a liquid usually has a volume that. While maintaining a definite volume, a liquid lacks a. It is characterized by its ability to retain almost a constant. A liquid is a state of matter that flows freely and takes the shape of its container but maintains a constant volume. Liquid adjective (money) in the form of money, rather than investments or property, or able to be changed into money easily: A liquid is a state of matter that has a definite volume, but no fixed shape. In other words, a liquid takes the shape of its. A liquid is one of the three main states of matter, along with solids and gases. Unlike a gas, a liquid usually has a volume that. A liquid is a state of matter that. A liquid is one of the three main states of matter, along with solids and gases. Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. Liquid commonly refers to substances, as water, oil, alcohol, and the like, that are neither solids nor gases: A liquid is a state of matter that. Liquid is a state of matter with a definite volume but no fixed shape. Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. Liquid, in physics, one of the three principal states of matter, intermediate between gas and crystalline solid. The meaning of liquid is flowing freely like water. A liquid. Liquid commonly refers to substances, as water, oil, alcohol, and the like, that are neither solids nor gases: While maintaining a definite volume, a liquid lacks a. Unlike a solid, a liquid has no fixed shape, but instead has a characteristic readiness to flow and therefore takes on the shape of any container. A liquid represents one of the fundamental. Examples of liquids include water, oil, and blood. A liquid represents one of the fundamental states of matter, characterized by particles that possess the ability to flow. A liquid is a state of matter that has a definite volume, but no fixed shape. Unlike a solid, a liquid has no fixed shape, but instead has a characteristic readiness to flow. A liquid is one of the three main states of matter, along with solids and gases. Liquid, in physics, one of the three principal states of matter, intermediate between gas and crystalline solid. Unlike a solid, a liquid has no fixed shape, but instead has a characteristic readiness to flow and therefore takes on the shape of any container. Unlike. It is characterized by its ability to retain almost a constant. It is made up of tiny particles, such as ions or molecules, that are close together but not as tightly packed as in solids. Unlike a gas, a liquid usually has a volume that. The most obvious physical properties of a liquid are its retention of volume. The meaning. A liquid is one of the three main states of matter, along with solids and gases. Liquid adjective (money) in the form of money, rather than investments or property, or able to be changed into money easily: A liquid is a state of matter that flows freely and takes the shape of its container but maintains a constant volume. A. Liquid, in physics, one of the three principal states of matter, intermediate between gas and crystalline solid. A liquid represents one of the fundamental states of matter, characterized by particles that possess the ability to flow. Unlike a solid, a liquid has no fixed shape, but instead has a characteristic readiness to flow and therefore takes on the shape of. Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. A liquid represents one of the fundamental states of matter, characterized by particles that possess the ability to flow. It is characterized by its ability to retain almost a constant. The meaning of liquid is flowing freely like water. Liquid adjective (money). A liquid is a state of matter that flows freely and takes the shape of its container but maintains a constant volume. Unlike a solid, a liquid has no fixed shape, but instead has a characteristic readiness to flow and therefore takes on the shape of any container. It is characterized by its ability to retain almost a constant. Unlike a gas, a liquid usually has a volume that. Liquid is a state of matter with a definite volume but no fixed shape. While maintaining a definite volume, a liquid lacks a. Water ceases to be a liquid when it is frozen or turned to steam. The meaning of liquid is flowing freely like water. Liquid adjective (money) in the form of money, rather than investments or property, or able to be changed into money easily: In other words, a liquid takes the shape of its. A liquid is one of the three main states of matter, along with solids and gases. A liquid represents one of the fundamental states of matter, characterized by particles that possess the ability to flow. Liquid commonly refers to substances, as water, oil, alcohol, and the like, that are neither solids nor gases: Liquid, in physics, one of the three principal states of matter, intermediate between gas and crystalline solid. Liquids adapt to the shape of their container and are nearly incompressible, maintaining their volume even under pressure. Examples of liquids include water, oil, and blood.Science, States of Matter, Solid, Liquid, Gas, Elementary, Anchor Chart, Educational Poster Etsy
Difference between Solid, Liquid, Gas in Table Form Teachoo
Properties of Solids, Liquids, Gases Compared Teachoo Science Solid liquid gas, Chemistry
Solid Liquid Gas Anchor Chart
Solid Liquid And Gases Diagram Explainer What Are The Diffe
Solid Liquid Gas Anchor Chart
States of Matter Lesson HESI NurseHub
Gas Vs Solid Diagram Gases Solids Liquid Solid Gas Vs Proper
Properties of Solids, Liquids, Gases Compared Teachoo Science
CHART, Solids, Liquids and Gases
How To Use Liquid In A Sentence.
A Liquid Is A State Of Matter That Has A Definite Volume, But No Fixed Shape.
It Is Made Up Of Tiny Particles, Such As Ions Or Molecules, That Are Close Together But Not As Tightly Packed As In Solids.
The Most Obvious Physical Properties Of A Liquid Are Its Retention Of Volume.
Related Post: