Hyponatremia Chart
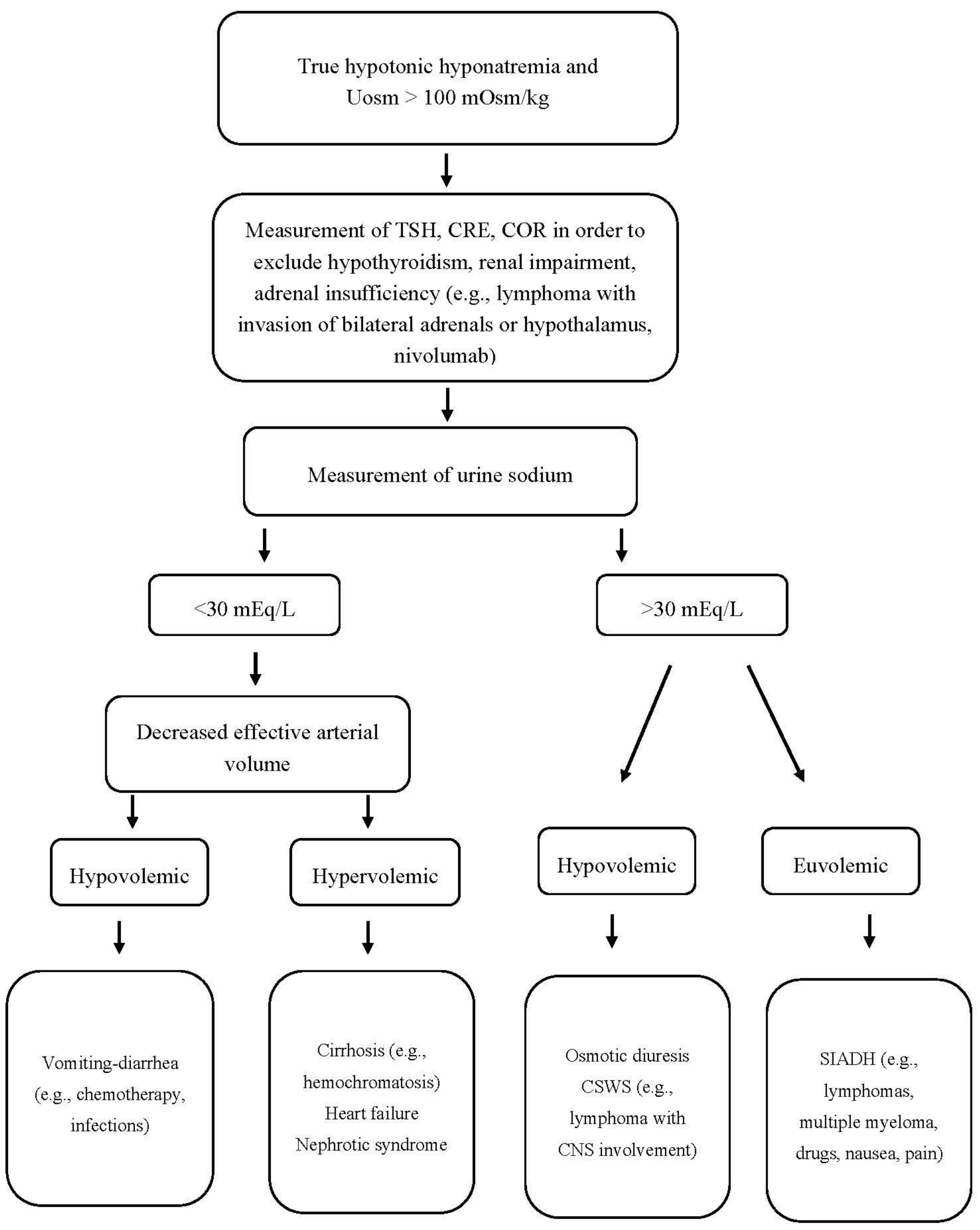
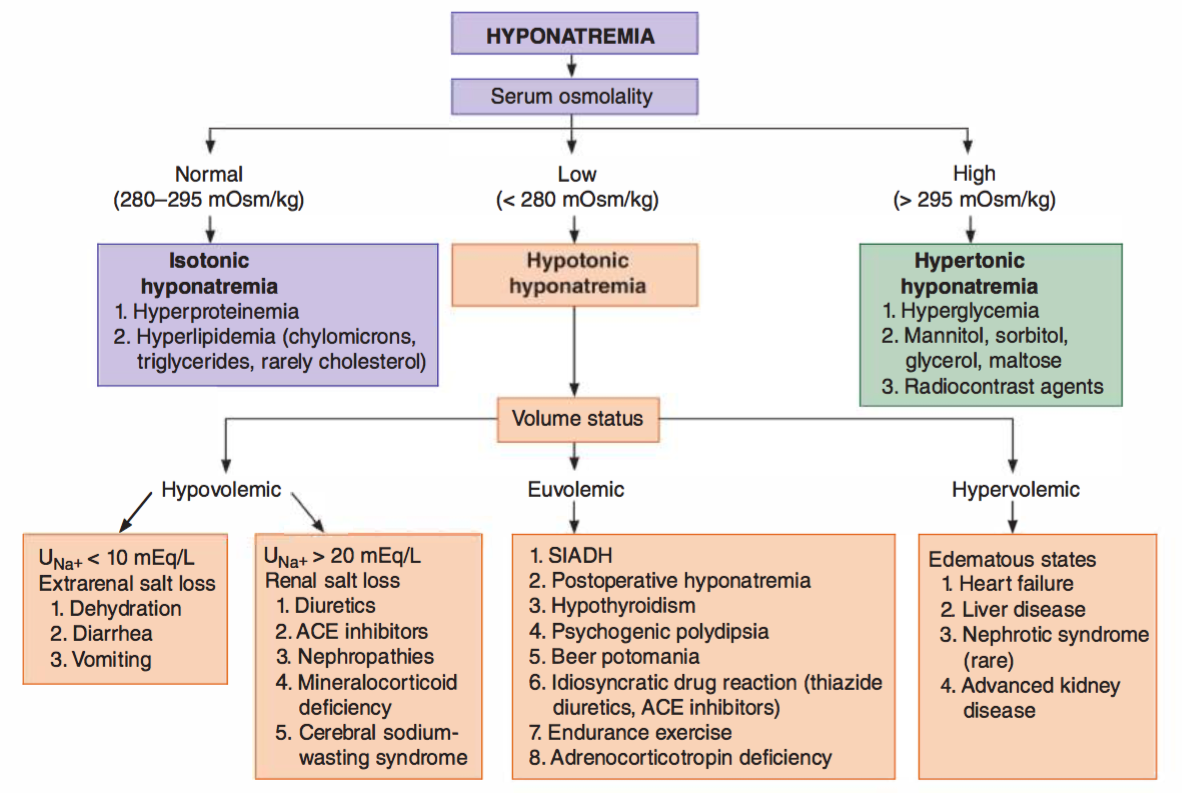
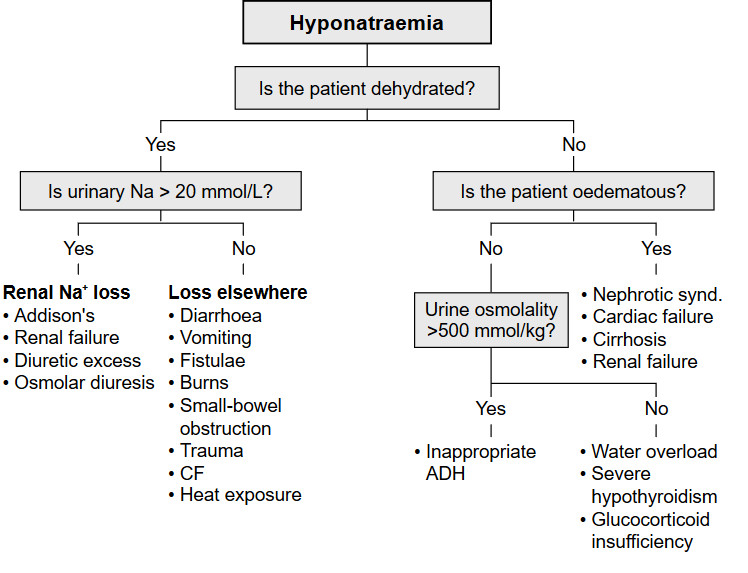
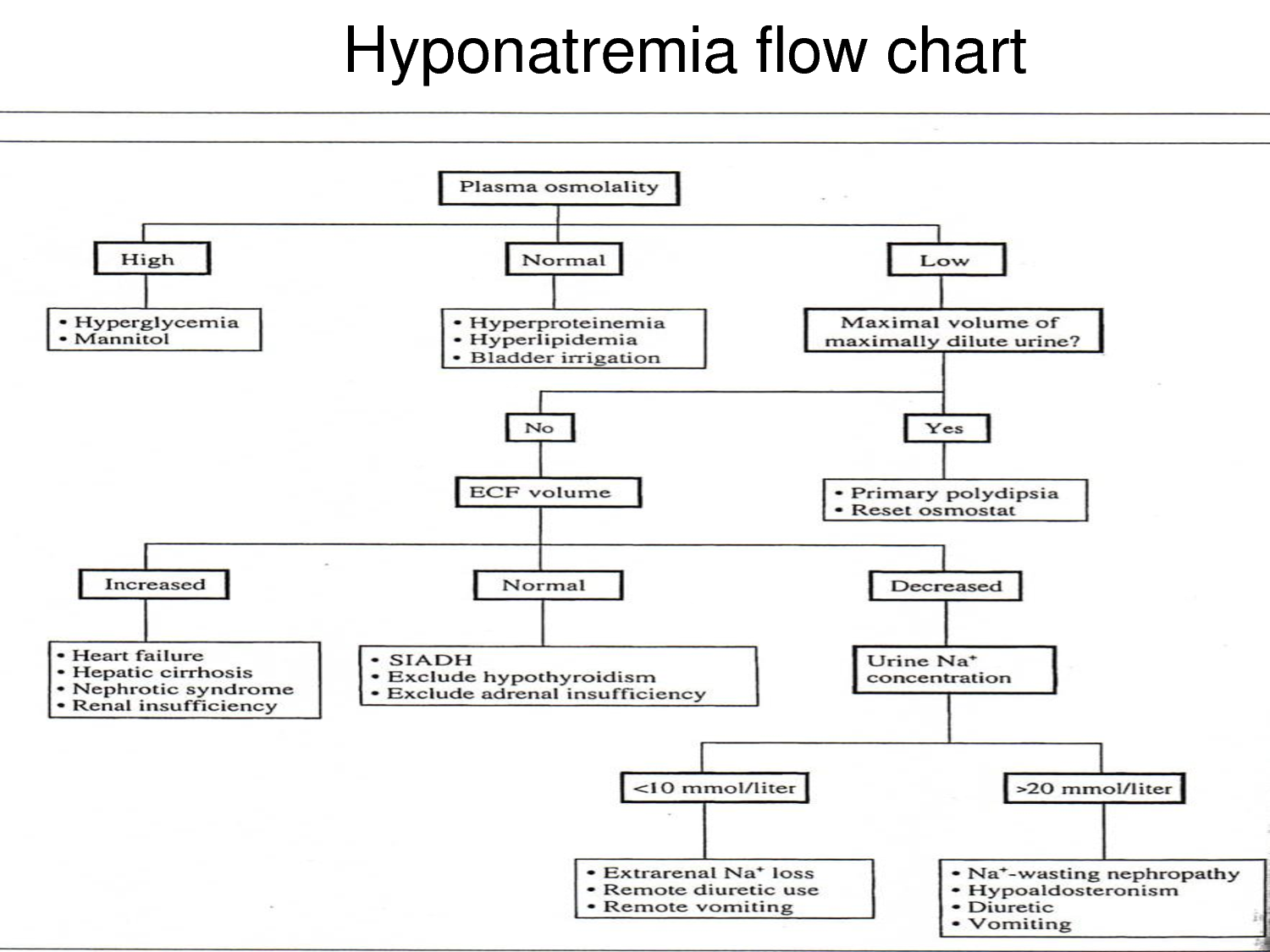
Hyponatremia Chart - It is the most common electrolyte abnormality encountered in clinical. Fluid status assess volume status. Hyponatremia and hypernatremia are common findings in the inpatient and outpatient settings. Hyponatremia, defined as a serum sodium concentration below 135 meq/l, is usually caused by a failure to excrete water normally [1,2]. Hyponatremia is when the amount of sodium in your blood is too low. Concentrated urine is found in most hyponatremic patients (including the three most common types of hyponatremia: These charts list sodium levels in milliequivalents per liter (meq/l). Sodium disorders are associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality. In healthy individuals, the ingestion. Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 meq/l but can vary to a small extent in different laboratories. In healthy individuals, the ingestion. Hyponatraemia occurs when there is a relative excess of water in the body compared to sodium. Management in primary care 1. It is the most common electrolyte abnormality encountered in clinical. Hyponatremia is the term used when your blood sodium is too low. Fluid status assess volume status. Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 meq/l but can vary to a small extent in different laboratories. These charts list sodium levels in milliequivalents per liter (meq/l). It’s key to look at: Concentrated urine is found in most hyponatremic patients (including the three most common types of hyponatremia: Hyponatraemia occurs when there is a relative excess of water in the body compared to sodium. It is the most common electrolyte abnormality encountered in clinical. Management in primary care 1. Common causes are fluid overload from ccf or dehydration from intercurrent illnesses and correct identification will. Concentrated urine is found in most hyponatremic patients (including the three most common. Hyponatremia, defined as a serum sodium concentration below 135 meq/l, is usually caused by a failure to excrete water normally [1,2]. It’s key to look at: Common causes are fluid overload from ccf or dehydration from intercurrent illnesses and correct identification will. Fluid status assess volume status. It is the most common electrolyte abnormality encountered in clinical. Hyponatremia, defined as a serum sodium concentration below 135 meq/l, is usually caused by a failure to excrete water normally [1,2]. Concentrated urine is found in most hyponatremic patients (including the three most common types of hyponatremia: It’s key to look at: Hypovolemic hyponatremia, euvolemic hyponatremia, and. Hyponatremia is a common electrolyte. Hyponatraemia occurs when there is a relative excess of water in the body compared to sodium. They also show normal, mild, moderate, and severe hyponatremia levels. Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 meq/l but can vary to a small extent in different laboratories. Hyponatremia is when the amount of sodium in your blood is. Common causes include heart, liver, kidney and brain diseases, hormone issues and medications. Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 meq/l but can vary to a small extent in different laboratories. Fluid status assess volume status. Hyponatremia is a common electrolyte. It’s key to look at: Common causes are fluid overload from ccf or dehydration from intercurrent illnesses and correct identification will. Hypovolemic hyponatremia, euvolemic hyponatremia, and. Management in primary care 1. Hyponatremia is the term used when your blood sodium is too low. Learn about symptoms, causes and treatment of this potentially dangerous condition. Fluid status assess volume status. These charts list sodium levels in milliequivalents per liter (meq/l). Management in primary care 1. Common causes include heart, liver, kidney and brain diseases, hormone issues and medications. Hyponatremia and hypernatremia are common findings in the inpatient and outpatient settings. Hyponatremia is the term used when your blood sodium is too low. These charts list sodium levels in milliequivalents per liter (meq/l). Concentrated urine is found in most hyponatremic patients (including the three most common types of hyponatremia: Hyponatremia and hypernatremia are common findings in the inpatient and outpatient settings. In healthy individuals, the ingestion. Hyponatremia is a common electrolyte. Hyponatraemia occurs when there is a relative excess of water in the body compared to sodium. Hyponatremia is the term used when your blood sodium is too low. Concentrated urine is found in most hyponatremic patients (including the three most common types of hyponatremia: Sodium disorders are associated with an increased risk of morbidity and. Learn about low sodium in the blood, its symptoms, causes, and treatment options for better health management. In healthy individuals, the ingestion. These charts list sodium levels in milliequivalents per liter (meq/l). Fluid status assess volume status. It’s key to look at: It is the most common electrolyte abnormality encountered in clinical. Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 meq/l but can vary to a small extent in different laboratories. Hyponatremia is when the amount of sodium in your blood is too low. Learn about symptoms, causes and treatment of this potentially dangerous condition. Sodium disorders are associated with an increased risk of morbidity and mortality. Learn about low sodium in the blood, its symptoms, causes, and treatment options for better health management. These charts list sodium levels in milliequivalents per liter (meq/l). It’s key to look at: Hyponatremia, defined as a serum sodium concentration below 135 meq/l, is usually caused by a failure to excrete water normally [1,2]. Hypovolemic hyponatremia, euvolemic hyponatremia, and. Hyponatremia is a common electrolyte. In healthy individuals, the ingestion. Fluid status assess volume status. Management in primary care 1. Hyponatremia is the term used when your blood sodium is too low. Concentrated urine is found in most hyponatremic patients (including the three most common types of hyponatremia:Diagnosis And Management Of Hyponatremia RECAPEM, 50 OFF
Urine Tests For Hyponatremia at Rachel Fairweather blog
Hyponatremia PsychDB
Hyponatremia Workup Chart Images and Photos finder
Maintenance Fluids For Hyponatremia at Winnie Norris blog
Diabetes Insipidus Hyponatremia
Delirium Hyponatremia at Marina Williams blog
Hyponatremia r/JuniorDoctorsUK
Hyponatremia Workup Chart Hyponatremia Causes Pathophysiology Algorithm
Hyponatremia Differential Diagnosis Chart sexiezpix Web Porn
Common Causes Are Fluid Overload From Ccf Or Dehydration From Intercurrent Illnesses And Correct Identification Will.
Hyponatremia And Hypernatremia Are Common Findings In The Inpatient And Outpatient Settings.
They Also Show Normal, Mild, Moderate, And Severe Hyponatremia Levels.
Hyponatraemia Occurs When There Is A Relative Excess Of Water In The Body Compared To Sodium.
Related Post: