Genotype Phenotype Chart
Genotype Phenotype Chart - The genotype of an organism is the chemical composition of its dna, which gives rise to the phenotype, or observable traits of an organism. The genotype determines the hereditary potentials and limitations of an individual from embryonic formation through adulthood. It can be represented by symbols. A genotype is a scoring of the type of variant present at a given location (i.e., a locus) in the genome. A genotype is the set of genes in our dna which is responsible for a particular trait. In genetics, the genotype and phenotype are two ways of describing an organism’s traits. It can refer to the entire genetic makeup of an individual or more specifically to the alleles. Biologists use the term genotype to distinguish from phenotype, which consists of the observable characteristics. For example, bb, bb, bb could be. Genotype is defined as the genetic constitution of an organism, encompassing the specific alleles present at particular loci on chromosomes. In other words, it describes an organism's complete set of genes. The genotype is the genetic code, while the phenotype is the physical. A genotype is a scoring of the type of variant present at a given location (i.e., a locus) in the genome. [1] genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic. A genotype is the genetic makeup of an individual organism. A genotype is the set of genes in our dna which is responsible for a particular trait. Among organisms that reproduce sexually, an individual’s. In genetics, the genotype and phenotype are two ways of describing an organism’s traits. A genotype consists of all the. Genotype is defined as the genetic constitution of an organism, encompassing the specific alleles present at particular loci on chromosomes. It can be represented by symbols. In a more narrow sense, the term. The genetic composition of an individual cell or organism that determines or influences its phenotype is known as its genotype. A genotype consists of all the. The genotype of an organism is the chemical composition of its dna, which gives rise to the phenotype, or observable traits. A genotype is the genetic makeup of an individual organism. It can refer to the entire genetic makeup of an individual or more specifically to the alleles. The genotype determines the hereditary potentials and limitations of an individual from embryonic formation through adulthood. The genotype of an organism is the chemical composition of its dna, which gives rise to the. From embryonic development to adulthood,. In a broad sense, the term genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism; It serves as the genetic blueprint that influences. For example, bb, bb, bb could be. A genotype is the genetic makeup of an individual organism. A genotype is a scoring of the type of variant present at a given location (i.e., a locus) in the genome. The genotype of an organism is the chemical composition of its dna, which gives rise to the phenotype, or observable traits of an organism. A genotype is the set of genes in our dna which is responsible for a. Biologists use the term genotype to distinguish from phenotype, which consists of the observable characteristics. A genotype is the set of genes in our dna which is responsible for a particular trait. In genetics, the genotype and phenotype are two ways of describing an organism’s traits. It can be represented by symbols. It serves as the genetic blueprint that influences. Genotype is defined as the genetic constitution of an organism, encompassing the specific alleles present at particular loci on chromosomes. The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. A genotype is the set of genes in our dna which is responsible for a particular trait. The genotype determines the hereditary potentials and limitations of an individual. Genotype is defined as the genetic constitution of an organism, encompassing the specific alleles present at particular loci on chromosomes. The genotype determines the hereditary potentials and limitations of an individual from embryonic formation through adulthood. For example, bb, bb, bb could be. In genetics, the genotype and phenotype are two ways of describing an organism’s traits. A genotype is. A genotype is the set of genes in our dna which is responsible for a particular trait. A genotype is a scoring of the type of variant present at a given location (i.e., a locus) in the genome. The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. [1] genotype can also be used to refer to the. In a more narrow sense, the term. In other words, it describes an organism's complete set of genes. The genotype of an organism is the chemical composition of its dna, which gives rise to the phenotype, or observable traits of an organism. In genetics, the genotype and phenotype are two ways of describing an organism’s traits. The genotype determines the. The genotype is the genetic code, while the phenotype is the physical. [1] genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic. It can refer to the entire genetic makeup of an individual or more specifically to the alleles. Genotype is defined as the genetic constitution of an. It can be represented by symbols. A genotype is the set of genes in our dna which is responsible for a particular trait. The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. A genotype consists of all the. The genetic composition of an individual cell or organism that determines or influences its phenotype is known as its genotype. It can refer to the entire genetic makeup of an individual or more specifically to the alleles. In genetics, the genotype and phenotype are two ways of describing an organism’s traits. The genotype determines the hereditary potentials and limitations of an individual from embryonic formation through adulthood. For example, bb, bb, bb could be. In a broad sense, the term genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism; The genotype is the genetic code, while the phenotype is the physical. In other words, it describes an organism's complete set of genes. The genotype of an organism is the chemical composition of its dna, which gives rise to the phenotype, or observable traits of an organism. Among organisms that reproduce sexually, an individual’s. A genotype is a scoring of the type of variant present at a given location (i.e., a locus) in the genome. In a more narrow sense, the term.Understanding Genotypes And Phenotypes
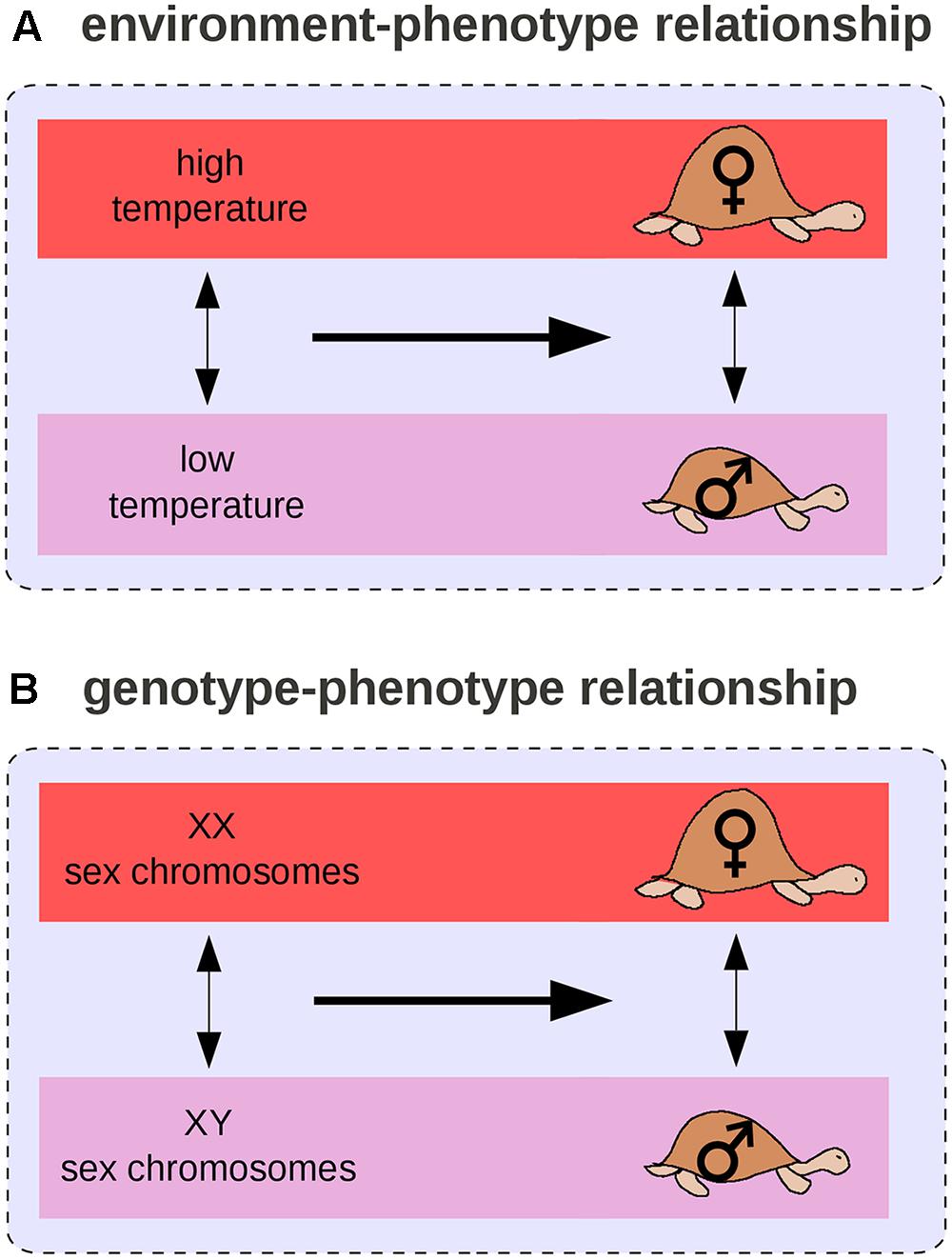
Frontiers The differential view of genotypephenotype relationships
Phenotype versus genotype stock vector. Illustration of genotype 251988660
PPT PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4736261
PPT Mendel and the Gene PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1751252
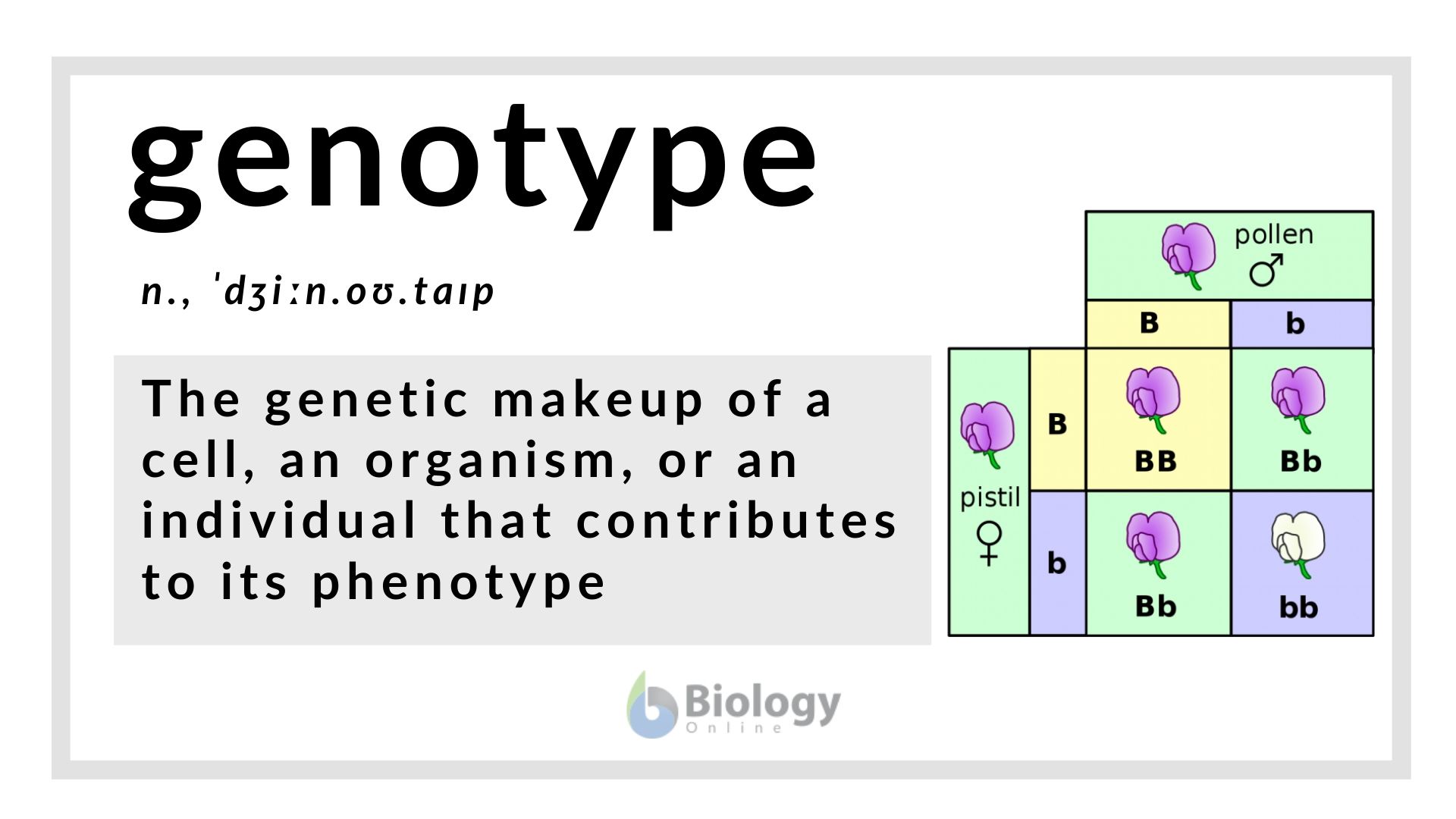
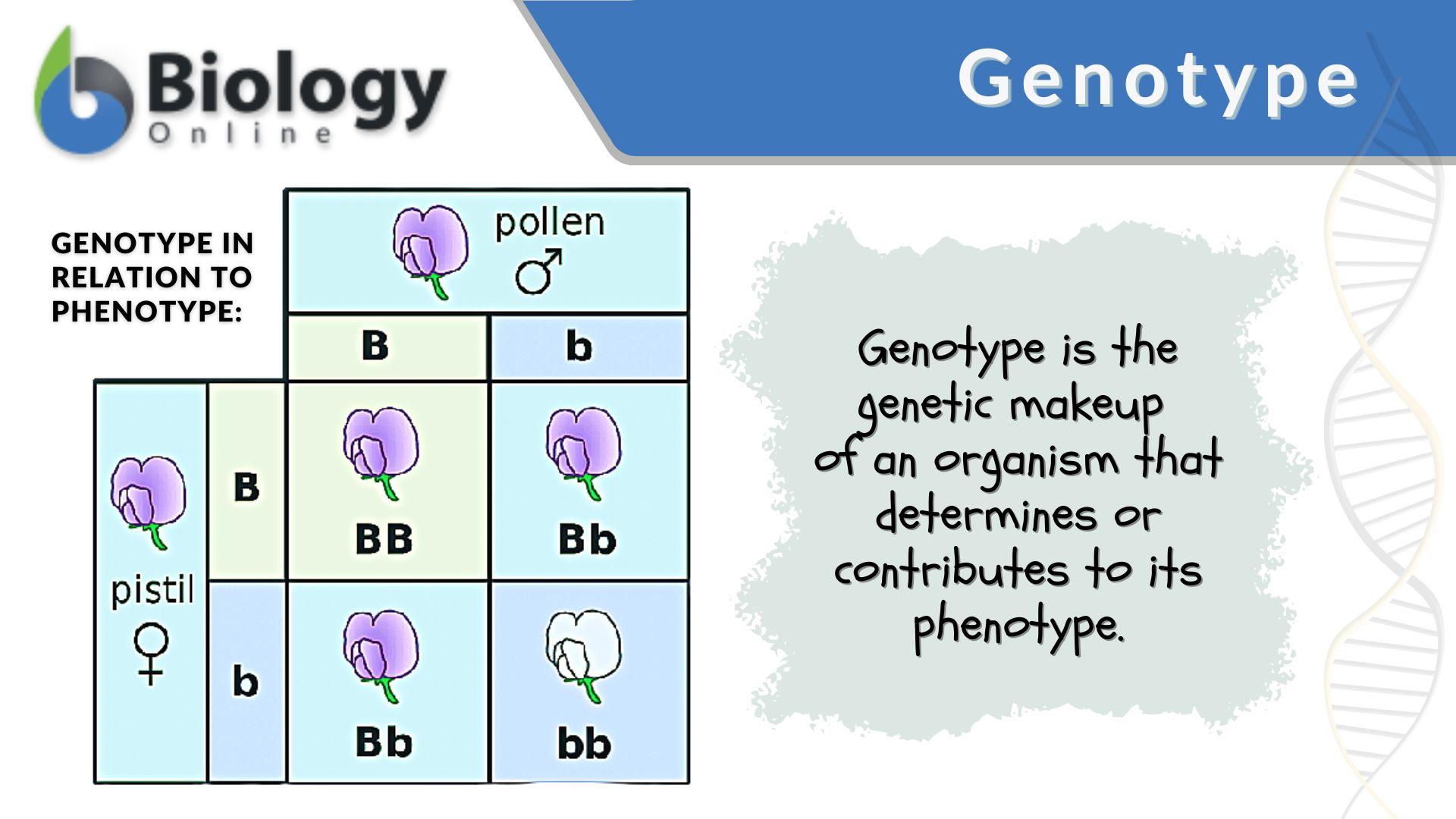
Genotype Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
PPT Chapter 11 Introduction to PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID261565
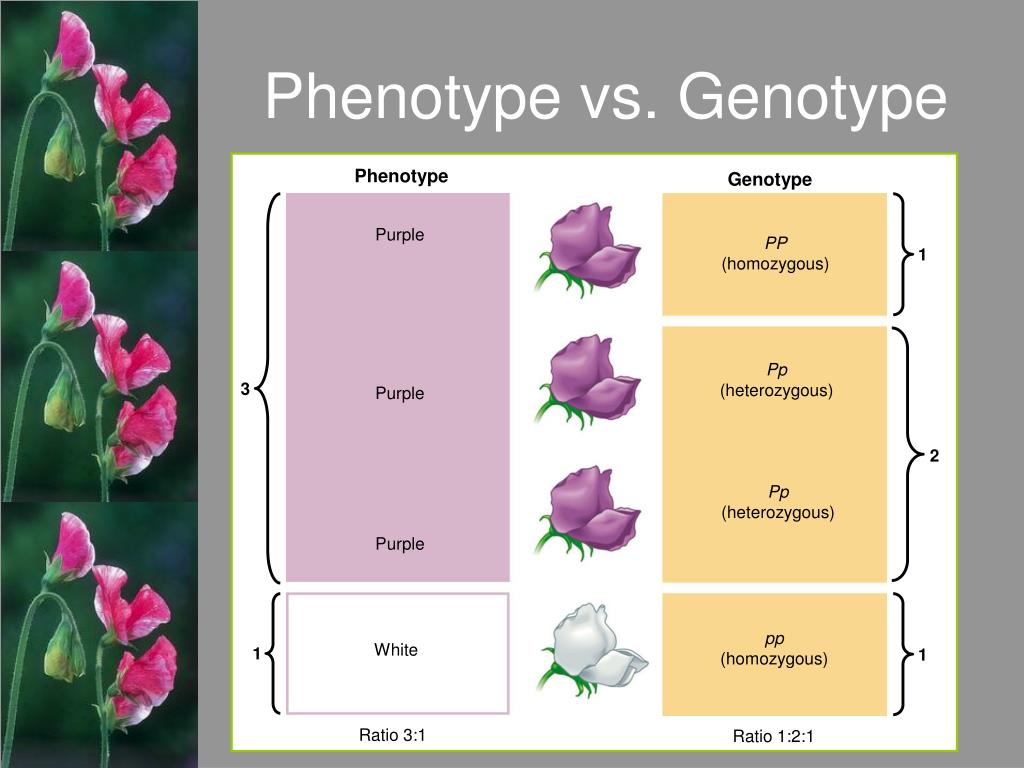
Genotype Vs Phenotype Square
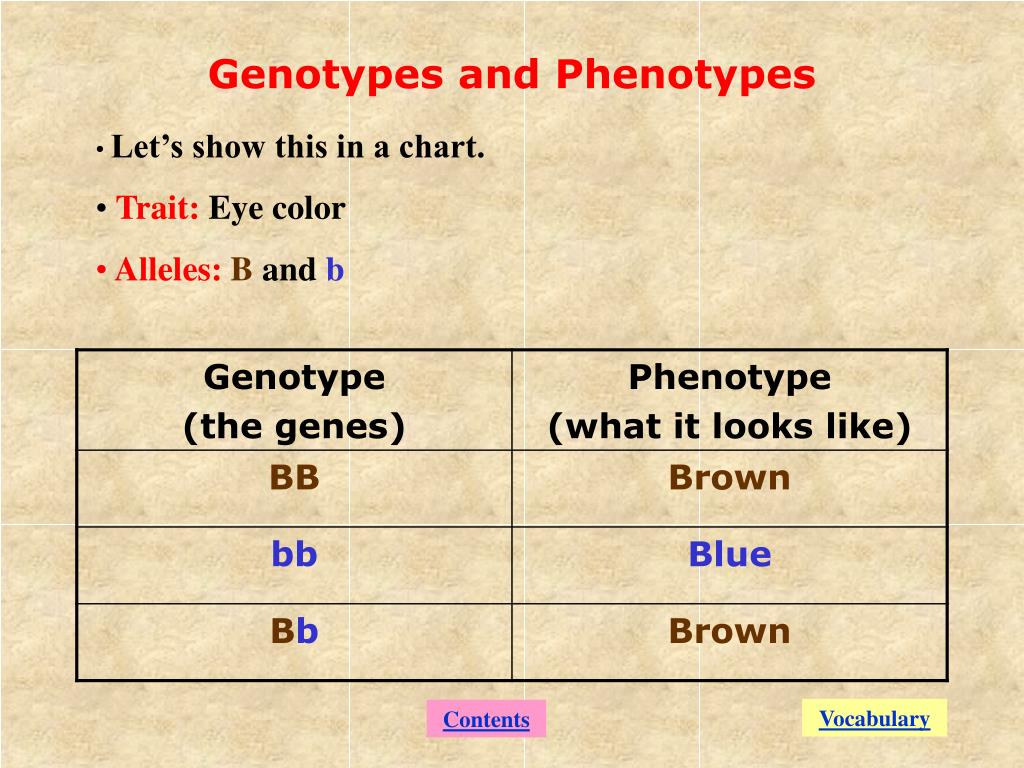
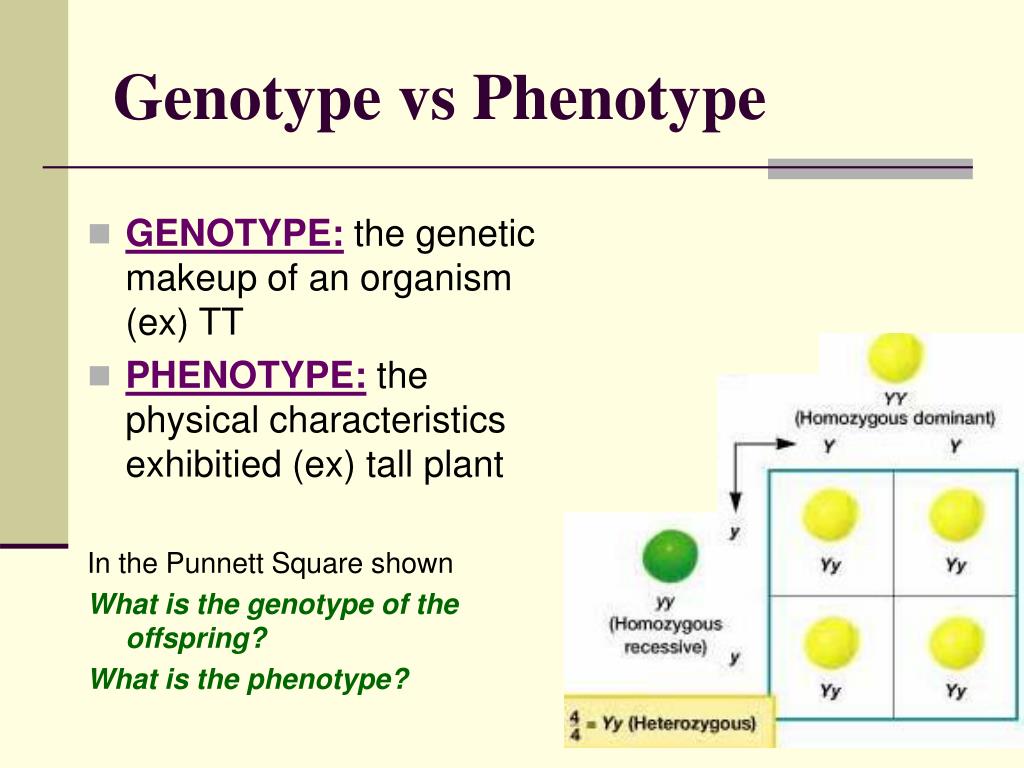
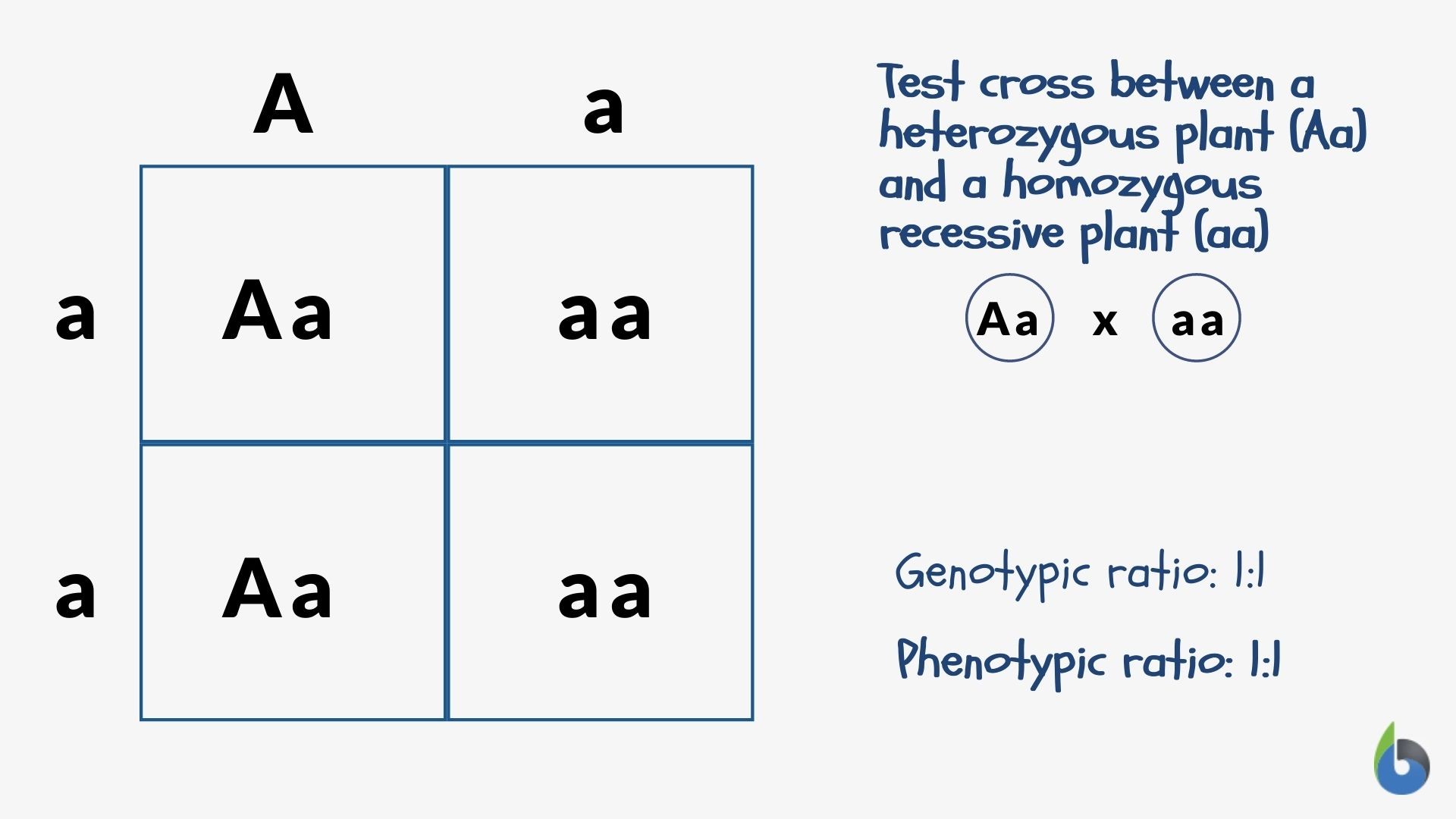
Genotype vs Phenotype Definitions and Examples
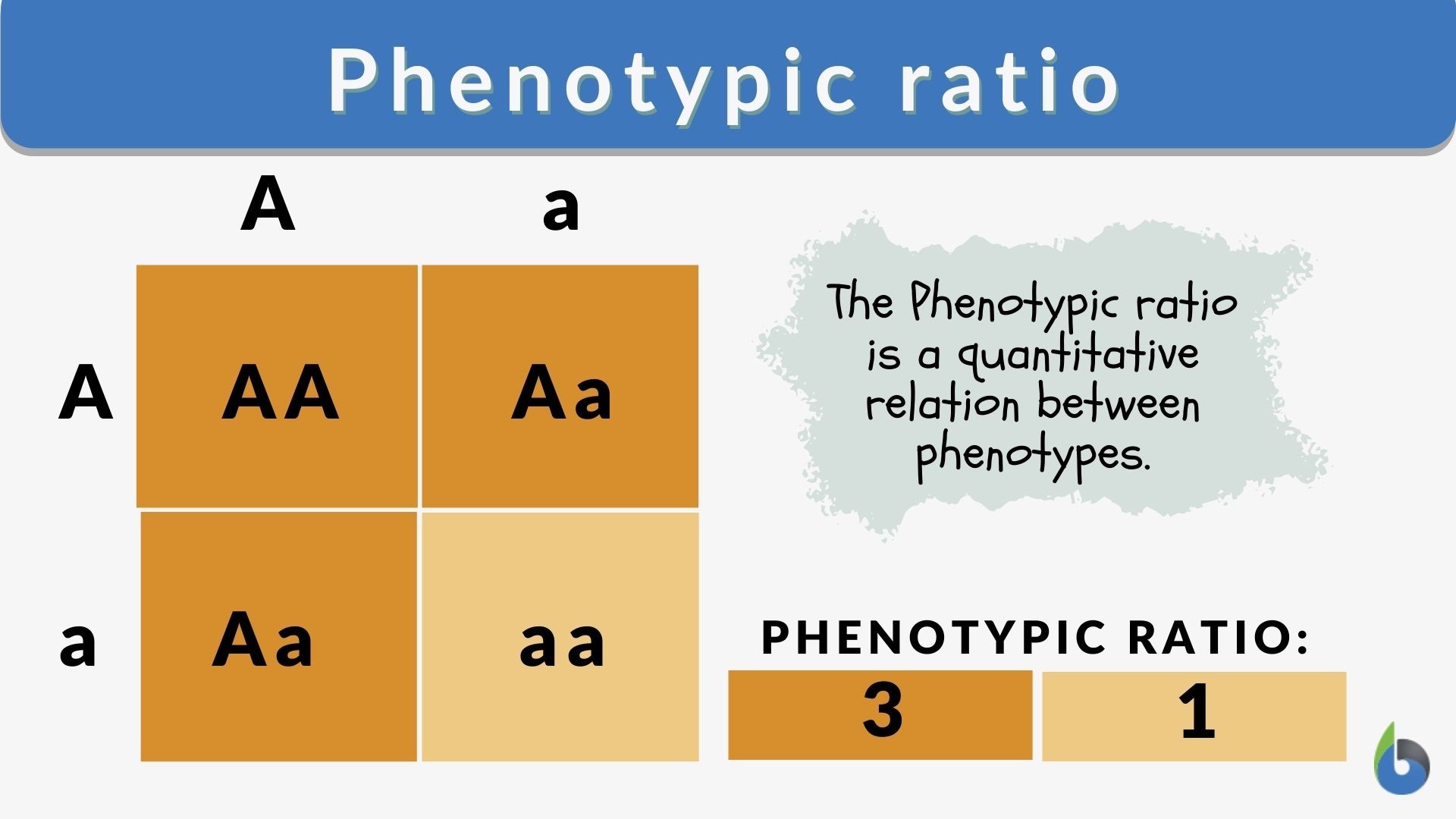
Phenotypic ratio Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Biologists Use The Term Genotype To Distinguish From Phenotype, Which Consists Of The Observable Characteristics.
It Serves As The Genetic Blueprint That Influences.
Genotype Is Defined As The Genetic Constitution Of An Organism, Encompassing The Specific Alleles Present At Particular Loci On Chromosomes.
[1] Genotype Can Also Be Used To Refer To The Alleles Or Variants An Individual Carries In A Particular Gene Or Genetic.
Related Post: