Elasticity Chart
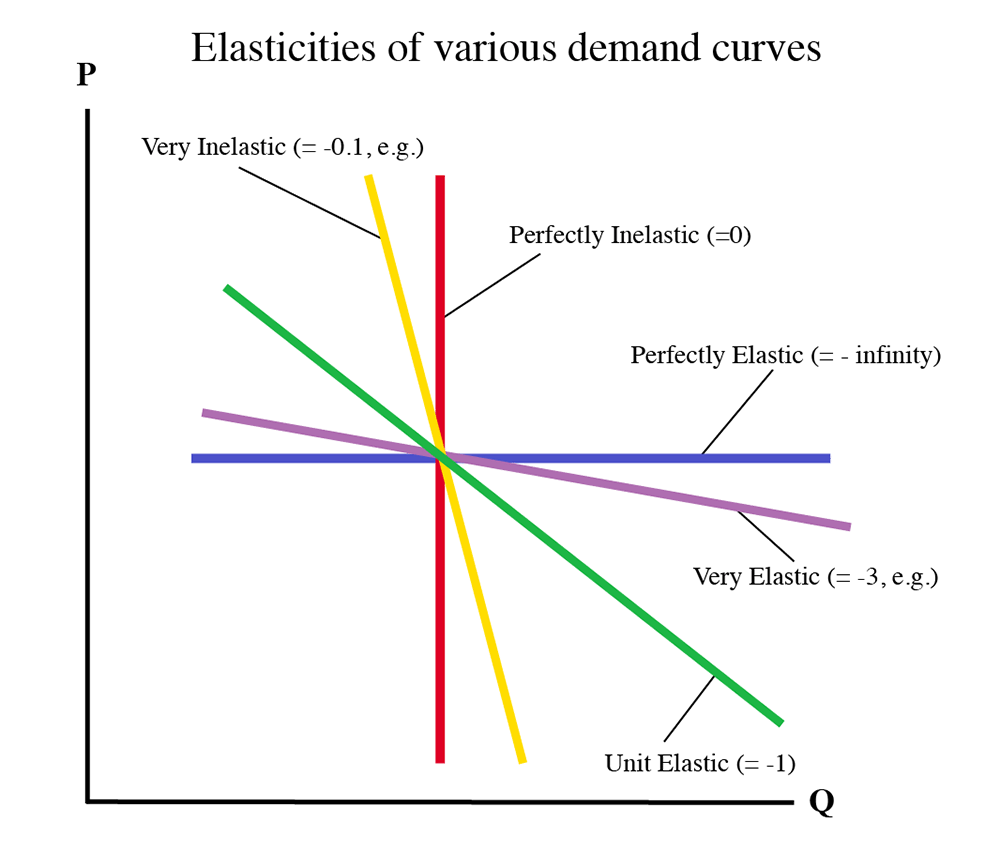
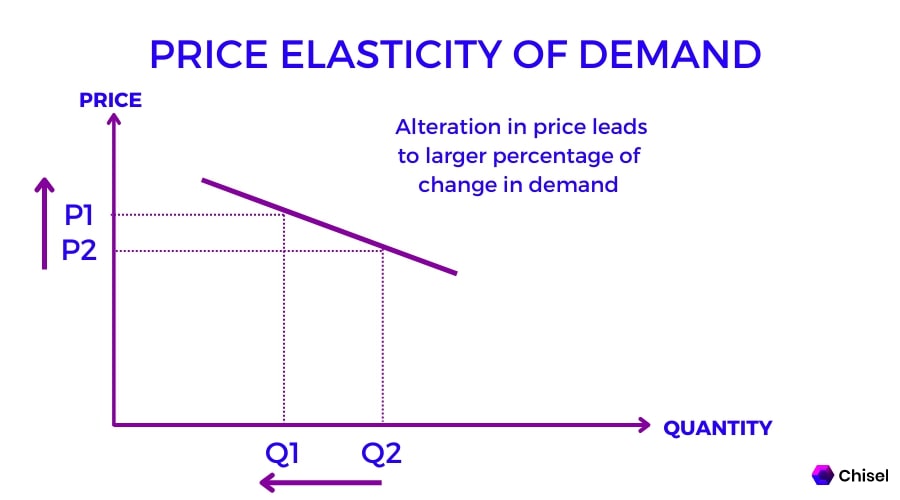
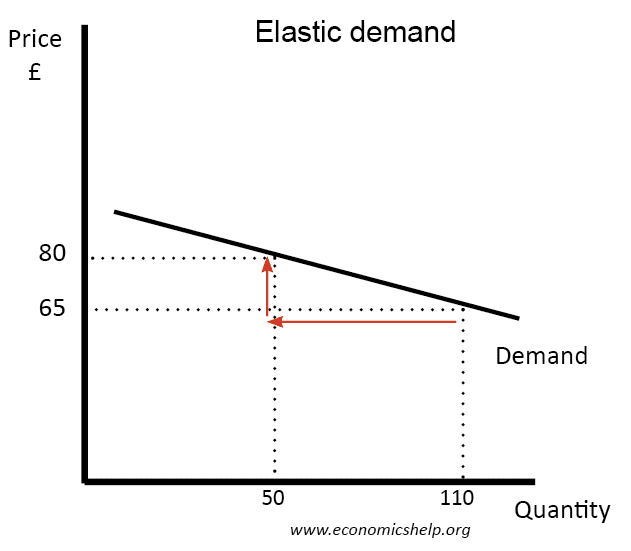
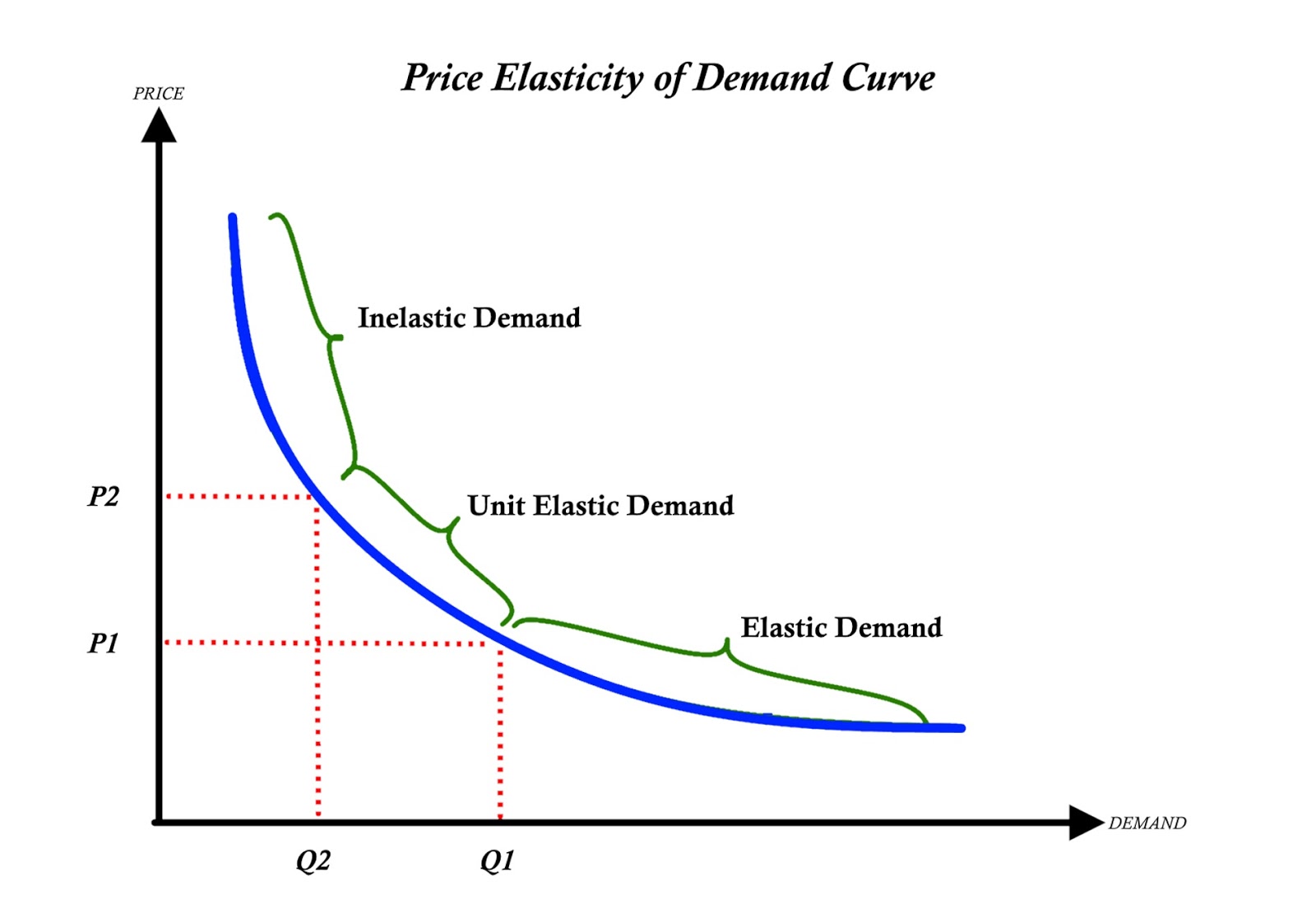
Elasticity Chart - Elasticity, in short, refers to the relative tendency of certain economic variables to change in response to other variables. Elasticity is a concept which involves examining how responsive demand (or supply) is to a change in another variable such as price or income. Elasticity in economics is a fundamental concept that measures how changes in price or other variables affect the behavior of buyers and sellers. Elasticity is a general measure of the responsiveness of an economic variable in response to a change in another economic variable. Elasticity is an economic term that describes the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another. Elasticity is a ratio of one percentage change to another percentage change—nothing more—and we read it as an absolute value. A variable y (e.g., the demand for a particular good) is elastic with respect to another variable x. Elasticity is an economics concept that measures the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another variable. In economics, elasticity measures the responsiveness of one economic variable to a change in another. It commonly refers to how demand changes in response to price. Elasticity is a ratio of one percentage change to another percentage change—nothing more—and we read it as an absolute value. In this case, a 1% rise in price causes an increase in quantity. Elasticity, in short, refers to the relative tendency of certain economic variables to change in response to other variables. A variable y (e.g., the demand for a particular good) is elastic with respect to another variable x. For example, if you raise the price of your product, how will that affect your. Elasticity is an economic term that describes the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another. Elasticity is an economics concept that measures the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another variable. Elasticity, in economics, a measure of the responsiveness of one economic variable to another. In economics, elasticity measures the responsiveness of one economic variable to a change in another. In economics, it is important to understand how. A variable y (e.g., the demand for a particular good) is elastic with respect to another variable x. Elasticity is an economic term that describes the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another. Elasticity is a general measure of the responsiveness of an economic variable in response to a change in another economic variable. Elasticity, in short, refers to. For example, if you raise the price of your product, how will that affect your. [1] for example, if the price elasticity of the demand of a good is −2, then a 10%. Elasticity is an economics concept that measures the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another variable. It commonly refers to how demand changes in response to. Elasticity is an economics concept that measures the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another variable. For example, if you raise the price of your product, how will that affect your. Elasticity, in short, refers to the relative tendency of certain economic variables to change in response to other variables. Elasticity is a measure of the change in one. Elasticity in economics is a fundamental concept that measures how changes in price or other variables affect the behavior of buyers and sellers. A variable y (e.g., the demand for a particular good) is elastic with respect to another variable x. Elasticity is a concept which involves examining how responsive demand (or supply) is to a change in another variable. A variable y (e.g., the demand for a particular good) is elastic with respect to another variable x. Elasticity, in economics, a measure of the responsiveness of one economic variable to another. Elasticity, in short, refers to the relative tendency of certain economic variables to change in response to other variables. In economics, it is important to understand how. Elasticity. It commonly refers to how demand changes in response to price. Elasticity is a measure of the change in one variable in response to a change in another, and it’s usually expressed as a ratio or percentage. Elasticity is a ratio of one percentage change to another percentage change—nothing more—and we read it as an absolute value. Elasticity, in short,. Elasticity in economics is a fundamental concept that measures how changes in price or other variables affect the behavior of buyers and sellers. Elasticity, in economics, a measure of the responsiveness of one economic variable to another. It commonly refers to how demand changes in response to price. The three major forms of elasticity are price elasticity of. In this. Elasticity is an economic term that describes the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another. Elasticity, in economics, a measure of the responsiveness of one economic variable to another. In economics, it is important to understand how. In this case, a 1% rise in price causes an increase in quantity. Elasticity in economics is a fundamental concept that measures. Elasticity, in short, refers to the relative tendency of certain economic variables to change in response to other variables. Elasticity is a concept which involves examining how responsive demand (or supply) is to a change in another variable such as price or income. Elasticity in economics is a fundamental concept that measures how changes in price or other variables affect. [1] for example, if the price elasticity of the demand of a good is −2, then a 10%. It commonly refers to how demand changes in response to price. Elasticity is a ratio of one percentage change to another percentage change—nothing more—and we read it as an absolute value. Elasticity, in short, refers to the relative tendency of certain economic. [1] for example, if the price elasticity of the demand of a good is −2, then a 10%. Elasticity is a measure of the change in one variable in response to a change in another, and it’s usually expressed as a ratio or percentage. The three major forms of elasticity are price elasticity of. It commonly refers to how demand changes in response to price. Elasticity is a concept which involves examining how responsive demand (or supply) is to a change in another variable such as price or income. In economics, it is important to understand how. Elasticity is an economic term that describes the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another. A variable y (e.g., the demand for a particular good) is elastic with respect to another variable x. Elasticity, in economics, a measure of the responsiveness of one economic variable to another. Elasticity is a ratio of one percentage change to another percentage change—nothing more—and we read it as an absolute value. Elasticity is a general measure of the responsiveness of an economic variable in response to a change in another economic variable. For example, if you raise the price of your product, how will that affect your. In economics, elasticity measures the responsiveness of one economic variable to a change in another.Price Elasticity of Demand E B F 200 Introduction to Energy and Earth Sciences Economics
Chart Of Demand Elasticity
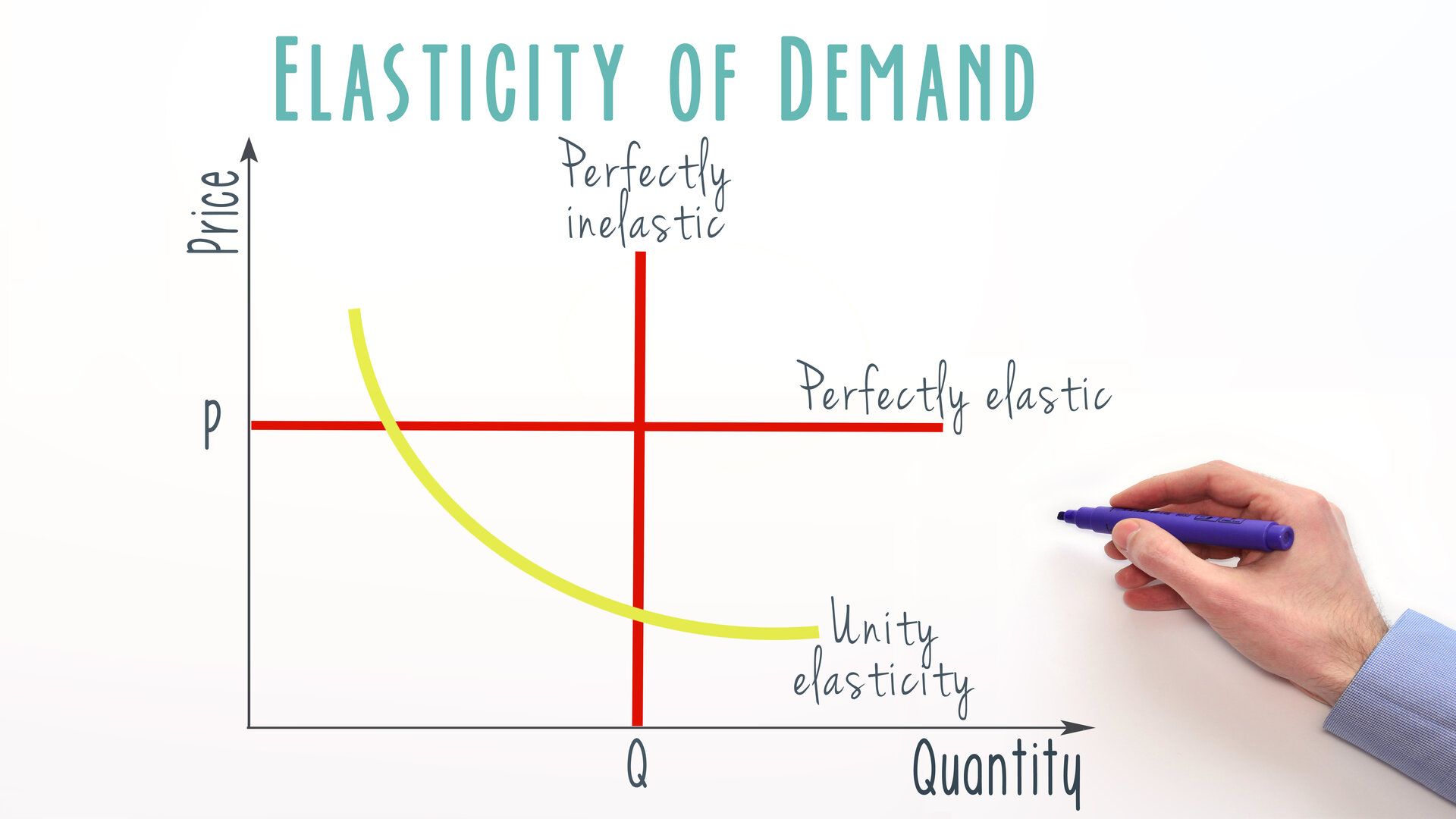
Understanding Elasticity Economics Help
How To Determine The Elasticity Of Demand
What Is Price Elasticity of Demand? Definition & Formula Glossary
Price Elasticity of DemandTypes and its Determinants Tutor's Tips
Chart Of Demand Elasticity
Chart Of Demand Elasticity
How To Determine The Elasticity Of Demand
Chart Of Demand Elasticity
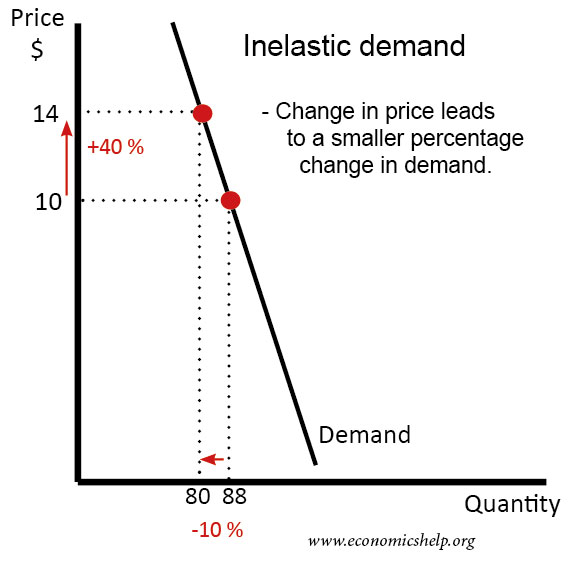
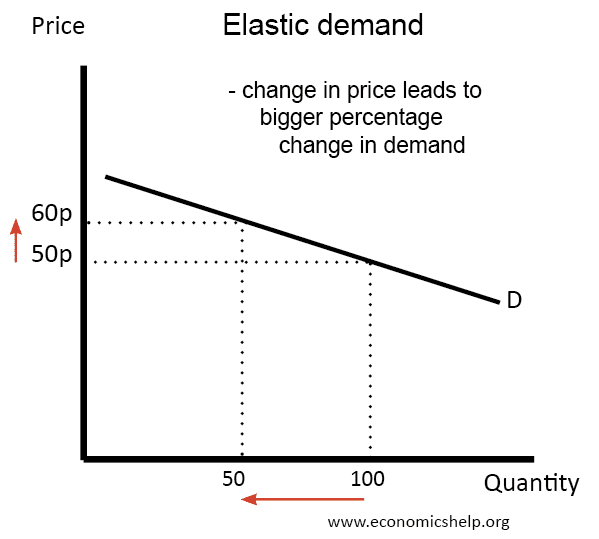
In This Case, A 1% Rise In Price Causes An Increase In Quantity.
Elasticity Is An Economics Concept That Measures The Responsiveness Of One Variable To Changes In Another Variable.
Elasticity, In Short, Refers To The Relative Tendency Of Certain Economic Variables To Change In Response To Other Variables.
Elasticity In Economics Is A Fundamental Concept That Measures How Changes In Price Or Other Variables Affect The Behavior Of Buyers And Sellers.
Related Post: