Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Chart
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Chart - An explanation of the functions of carbohydrates, the dangers of too many carbs and the recommended carb intake. Foods that contain high amounts of simple carbs (added sugars), especially fructose, raise triglyceride levels, which. They act as an energy source, help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism, participate in cholesterol and. Carbohydrates also are the parts of food that the body doesn't digest, called fiber. Carbs, or carbohydrates, are molecules that have carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Carbohydrates — fiber, starches and sugars — are essential food nutrients. Carbohydrates are the most widespread organic substances and play a vital role in all life. Your body turns carbs into glucose (blood sugar) to give you the energy you need to function. Carbohydrates are sugars in food. A carbohydrate (/ ˌkɑːrboʊˈhaɪdreɪt /) is a biomolecule composed of carbon (c), hydrogen (h), and oxygen (o) atoms. Carbohydrates are sugars in food. Carbohydrates are the most widespread organic substances and play a vital role in all life. The latest research on the effects of eating carbohydrates. Foods that contain high amounts of simple carbs (added sugars), especially fructose, raise triglyceride levels, which. Carbohydrates—fiber, sugars, and starch—are the body’s preferred fuel. Carbohydrates play an important role in the human body. Carbs, or carbohydrates, are molecules that have carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. The type of carbohydrates you eat can impact your health. Carbohydrates — fiber, starches and sugars — are essential food nutrients. Carbohydrates also are the parts of food that the body doesn't digest, called fiber. What does the word carbohydrate mean? Find out which types of carbs are best. An explanation of the functions of carbohydrates, the dangers of too many carbs and the recommended carb intake. Carbohydrates—fiber, sugars, and starch—are the body’s preferred fuel. Carbohydrates play an important role in the human body. They act as an energy source, help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism, participate in cholesterol and. Foods that contain high amounts of simple carbs (added sugars), especially fructose, raise triglyceride levels, which. Your body turns carbs into glucose (blood sugar) to give you the energy you need to function. Carbohydrates are the most widespread organic substances and play a. They act as an energy source, help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism, participate in cholesterol and. Your body turns carbs into glucose (blood sugar) to give you the energy you need to function. The latest research on the effects of eating carbohydrates. The type of carbohydrates you eat can impact your health. In nutrition, the word “carbs” refers to. In nutrition, the word “carbs” refers to one of the three macronutrients. An explanation of the functions of carbohydrates, the dangers of too many carbs and the recommended carb intake. What does the word carbohydrate mean? Your body turns carbs into glucose (blood sugar) to give you the energy you need to function. Find out which types of carbs are. Carbohydrates—fiber, sugars, and starch—are the body’s preferred fuel. Carbohydrates also are the parts of food that the body doesn't digest, called fiber. Carbohydrates are the most widespread organic substances and play a vital role in all life. They act as an energy source, help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism, participate in cholesterol and. Foods that contain high amounts of. Foods that contain high amounts of simple carbs (added sugars), especially fructose, raise triglyceride levels, which. Find out which types of carbs are best. Carbohydrates are sugars in food. An explanation of the functions of carbohydrates, the dangers of too many carbs and the recommended carb intake. What does the word carbohydrate mean? Carbohydrates are sugars in food. Foods that contain high amounts of simple carbs (added sugars), especially fructose, raise triglyceride levels, which. In nutrition, the word “carbs” refers to one of the three macronutrients. They act as an energy source, help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism, participate in cholesterol and. Carbohydrates play an important role in the human body. They act as an energy source, help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism, participate in cholesterol and. The type of carbohydrates you eat can impact your health. Carbohydrates are the most widespread organic substances and play a vital role in all life. Carbohydrates also are the parts of food that the body doesn't digest, called fiber. Carbohydrates play an important. In nutrition, the word “carbs” refers to one of the three macronutrients. An explanation of the functions of carbohydrates, the dangers of too many carbs and the recommended carb intake. What does the word carbohydrate mean? The latest research on the effects of eating carbohydrates. Carbohydrates—fiber, sugars, and starch—are the body’s preferred fuel. Carbohydrates—fiber, sugars, and starch—are the body’s preferred fuel. Carbohydrates also are the parts of food that the body doesn't digest, called fiber. Carbohydrates play an important role in the human body. Find out which types of carbs are best. Your body turns carbs into glucose (blood sugar) to give you the energy you need to function. An explanation of the functions of carbohydrates, the dangers of too many carbs and the recommended carb intake. What does the word carbohydrate mean? Carbohydrates are sugars in food. In nutrition, the word “carbs” refers to one of the three macronutrients. Carbohydrates are the most widespread organic substances and play a vital role in all life. Carbohydrates—fiber, sugars, and starch—are the body’s preferred fuel. Carbohydrates — fiber, starches and sugars — are essential food nutrients. They act as an energy source, help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism, participate in cholesterol and. Find out which types of carbs are best. Carbohydrates play an important role in the human body. A carbohydrate (/ ˌkɑːrboʊˈhaɪdreɪt /) is a biomolecule composed of carbon (c), hydrogen (h), and oxygen (o) atoms. The latest research on the effects of eating carbohydrates. Carbs, or carbohydrates, are molecules that have carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.Compare The Chemical Structure And Functions Of Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins And Nucleic Acids Structure at Keena Bryant blog
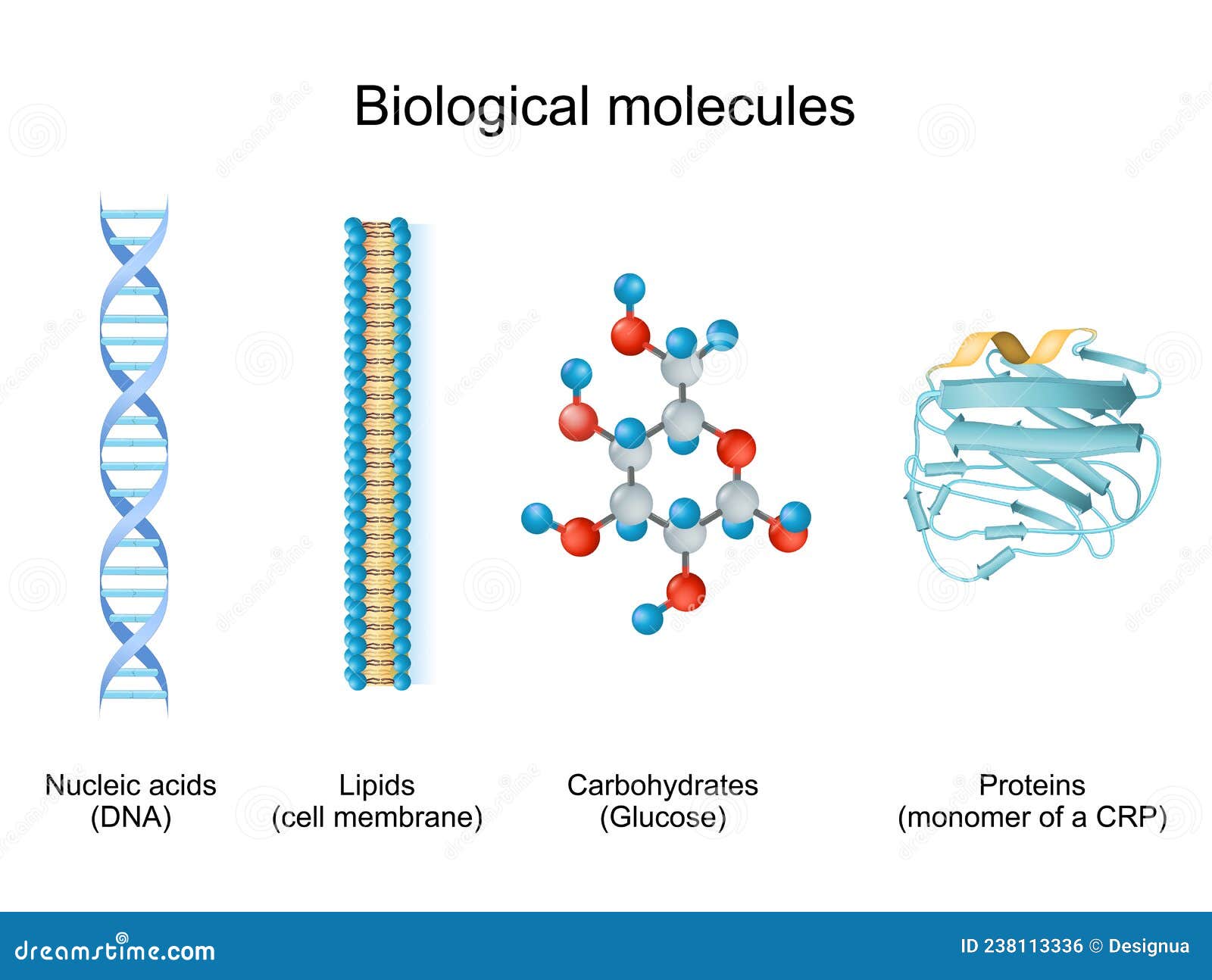
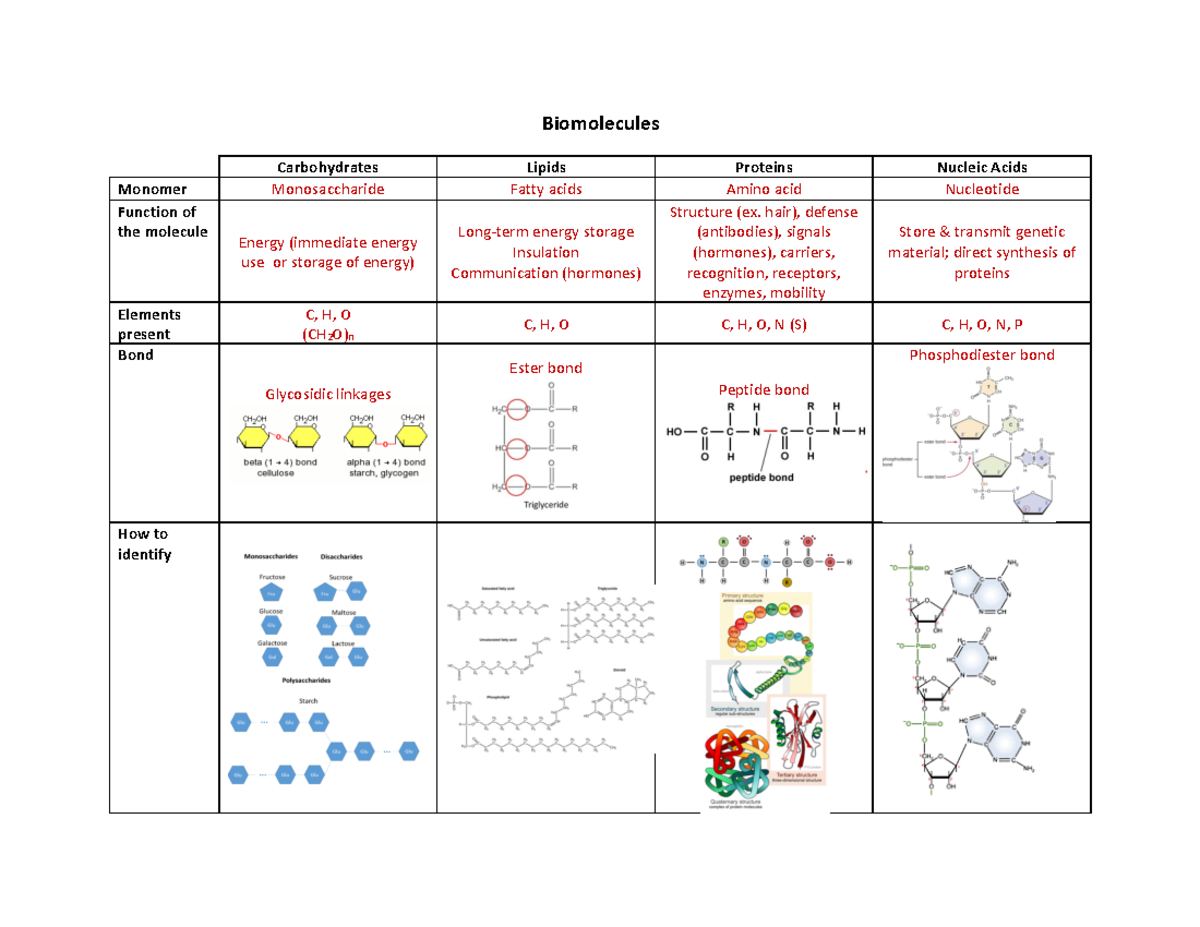
Biomolecule Chemical Structure Carbohydrate Protein Lipid Nucleic Acid
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins And Nucleic Acids Structure at Keena Bryant blog
Nucleic Acids Glucose at Glenn Barbee blog
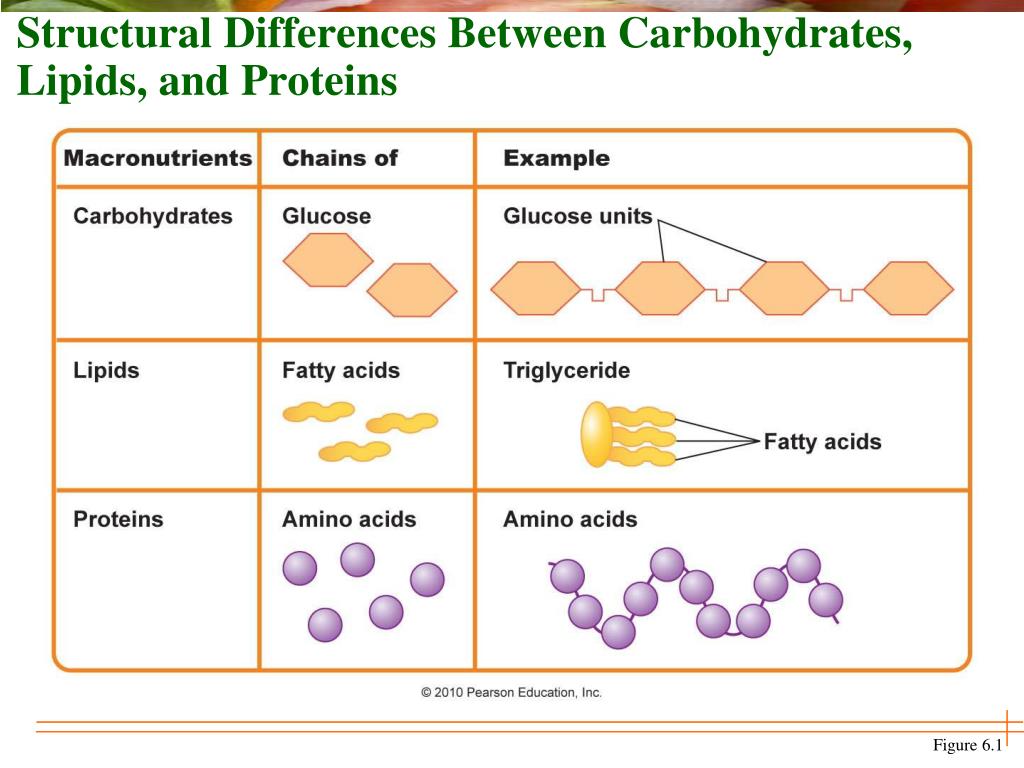
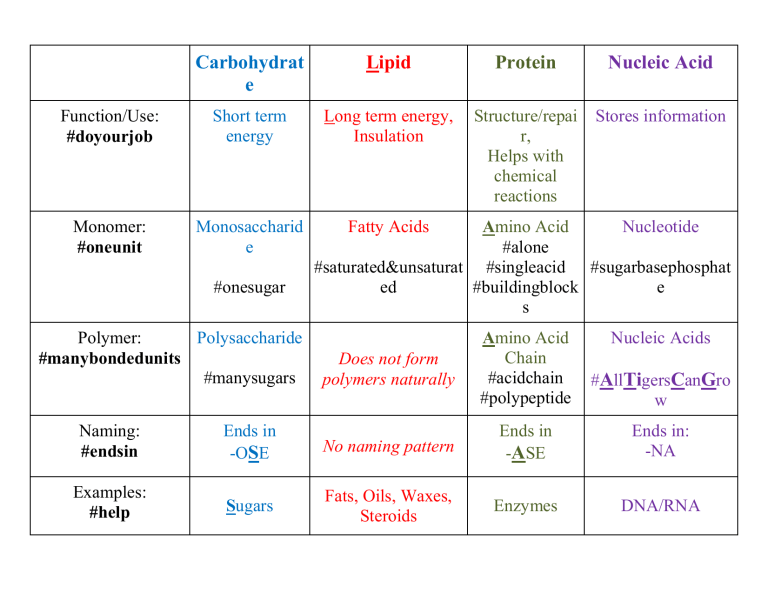
Table of Biomolecule, Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids Diagram Quizlet
Carbs Lipids And Proteins Venn Diagram Carbohydrates, Lipids
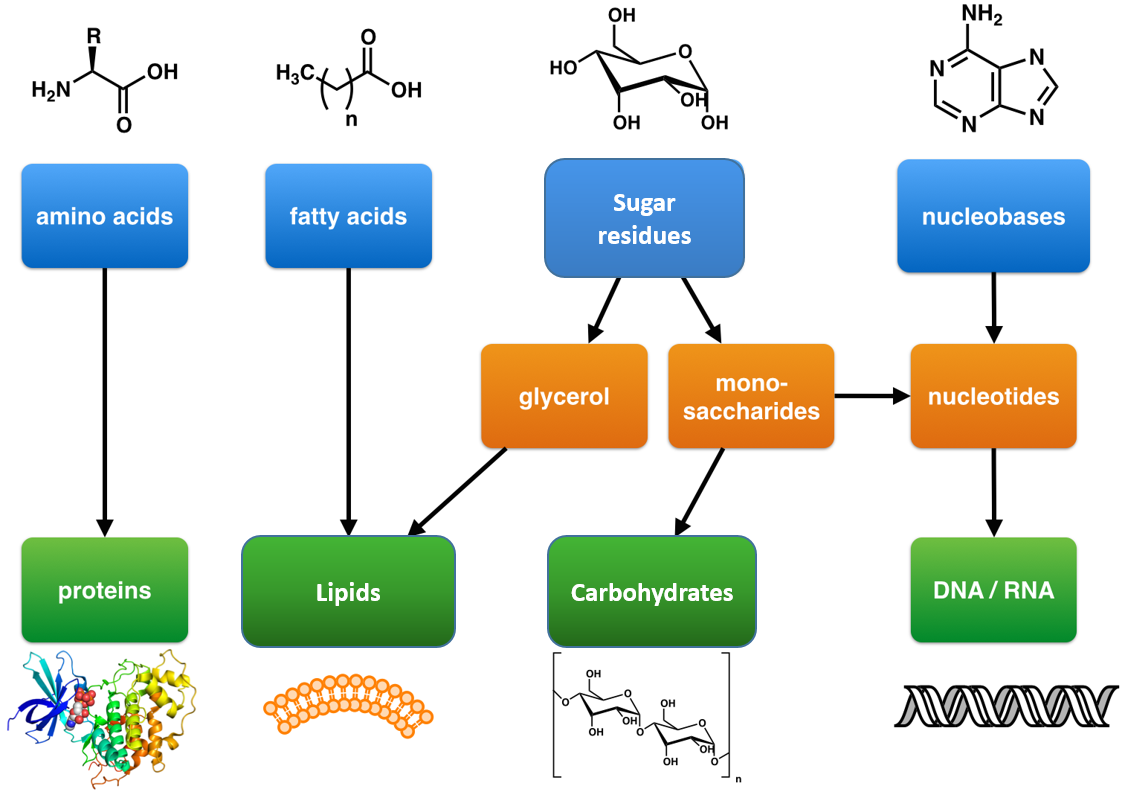
Four Biomolecules Structure and Function Comparison Chart Carbohydrates vs Proteins vs Nucleic
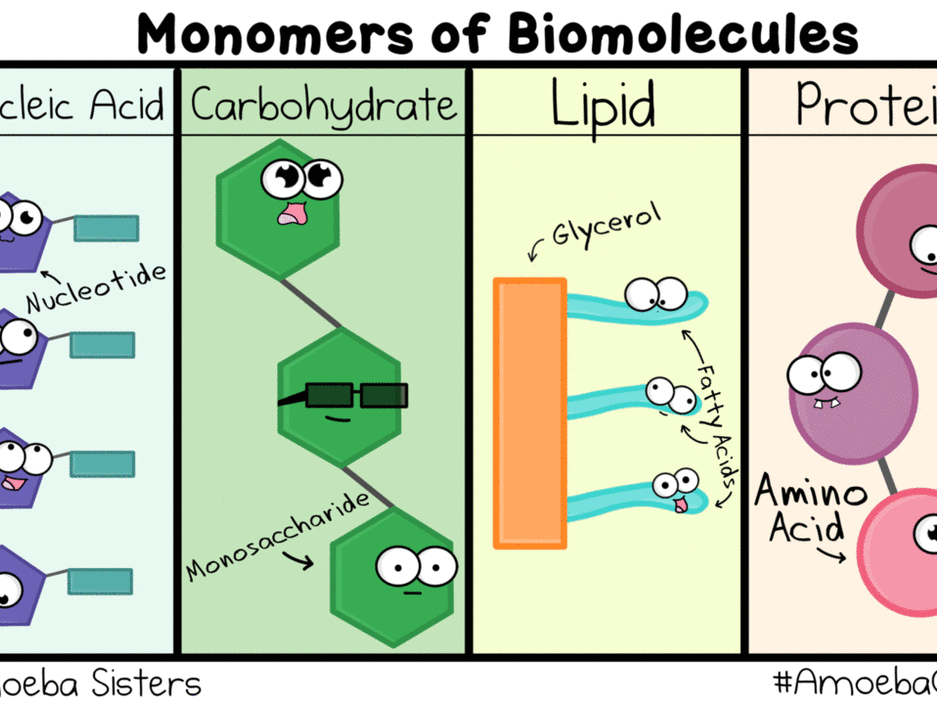
Biomolecules Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
5 Biomolecules chart Biomolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Monomer Studocu
Carbohydrates Also Are The Parts Of Food That The Body Doesn't Digest, Called Fiber.
Your Body Turns Carbs Into Glucose (Blood Sugar) To Give You The Energy You Need To Function.
Foods That Contain High Amounts Of Simple Carbs (Added Sugars), Especially Fructose, Raise Triglyceride Levels, Which.
The Type Of Carbohydrates You Eat Can Impact Your Health.
Related Post: